What does molarity measure the concentration of?
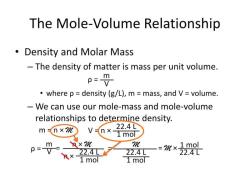
Molarity (M) is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution. Specifically, it represents the number of moles of solute dissolved in one liter of solution. The formula for calculating molarity is:
In this formula:
- Molarity (M) is expressed in moles per liter (mol/L or M).
- Moles of solute refer to the amount of the substance being dissolved in the solution.
- Liters of solution refer to the total volume of the solution.
Molarity provides a convenient way to express the concentration of a solution, and it is widely used in chemistry for various applications, including chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and laboratory work. It allows scientists and researchers to work with consistent and standardized units when dealing with solutions of different substances.
Concentration measurement: What does molarity measure the concentration of?
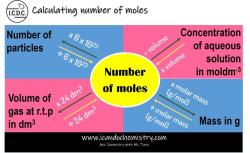
Molarity, also known as molar concentration, is a unit of concentration that expresses the number of moles of a solute per liter of solution. It is one of the most common ways to express the concentration of a solution in chemistry. The formula for molarity is:
M = n/V
where:
- M is molarity (mol/L)
- n is the number of moles of solute (mol)
- V is the volume of solution (L)
For example, if you have 1 mole of NaCl dissolved in 1 liter of water, then the molarity of the solution is 1 M.
Molarity is a convenient way to express the concentration of a solution because it is based on the mole, which is a fundamental unit in chemistry. The mole is defined as the amount of substance that contains 6.022 x 10^23 atoms or molecules. This means that 1 mole of any substance contains the same number of atoms or molecules.
Molarity is also a versatile unit of concentration because it can be used to express the concentration of solutions of any solute, regardless of the solute's molecular weight. For example, the molarity of a solution of NaCl is the same as the molarity of a solution of glucose, even though the two solutes have different molecular weights.
Exploring the role of molarity in measuring the concentration of solutions
Molarity is a crucial tool for chemists and students in various fields, including analytical chemistry, biochemistry, and environmental chemistry. It allows for precise quantification of solutes in solutions, enabling accurate calculations and predictions in chemical reactions, laboratory experiments, and industrial processes.
Here are some specific examples of how molarity is used in measuring the concentration of solutions:
Preparing solutions with specific concentrations: Molarity is used to prepare solutions with defined concentrations for various applications, such as titrations, spectroscopic analyses, and buffer solutions.
Calculating reaction stoichiometry: Molarity is essential for calculating the stoichiometry of chemical reactions, determining the amount of reactants and products involved.
Analyzing solution composition: Molarity is used to analyze the composition of solutions, determining the concentration of specific solutes in mixtures.
Expressing solution concentrations in standardized units: Molarity provides a standardized way to express solution concentrations, ensuring consistency and clarity in scientific communication.
Tips for students and chemists in interpreting and using molarity in laboratory work
Understand the concept of moles and molar mass: Familiarize yourself with the concept of moles and molar mass to effectively use molarity in calculations.
Master the formula for molarity: Memorize the formula for molarity (M = n/V) and practice applying it to various scenarios.
Use molarity to prepare solutions: Learn how to prepare solutions of desired concentrations using molarity calculations.
Interpret molarity in reaction stoichiometry: Understand how molarity is used to calculate the amount of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
Communicate concentration using molarity: Express solution concentrations using molarity in laboratory reports and scientific discussions.