What is the formula for calculating molar mass?
The formula for calculating molar mass depends on the type of substance you are dealing with. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance and is expressed in units of grams per mole (g/mol). Here are the general formulas for calculating molar mass:
For Elements:
- The molar mass of an element is numerically equal to its atomic mass (in atomic mass units, amu).
- Molar Mass = Atomic Mass (in amu)
For Compounds:
For molecular compounds (covalent compounds):
- Add up the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule.
For ionic compounds:
- Add up the atomic masses of all the atoms in a formula unit.
Molar Mass = Sum of Atomic Masses of All Atoms in the Formula
Example:
- For water (H₂O), you would add the atomic masses of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
For Ionic Compounds:
For ionic compounds, the molar mass is the sum of the atomic masses of all the ions in a formula unit.
Example:
- For sodium chloride (NaCl), you would add the atomic mass of sodium and chlorine.
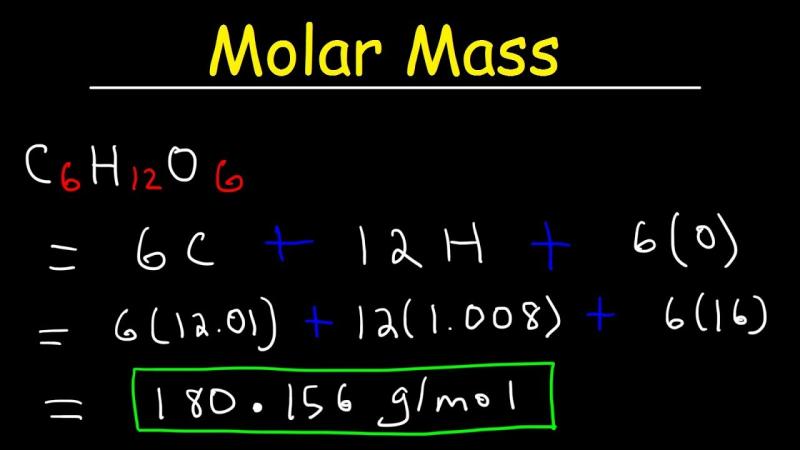
In summary, the key is to sum up the atomic masses of the individual atoms in a molecule or formula unit. The atomic masses can be found on the periodic table, typically in units of atomic mass units (amu). Once you add up these atomic masses, you get the molar mass of the substance in grams per mole.
Molecular mass calculation: What is the formula for calculating molar mass?
Formula for calculating molar mass:
Molar mass = (number of atoms of each element) x (atomic mass of each element)
The atomic mass of each element can be found on the periodic table.
For example, the molar mass of water (H2O) is calculated as follows:
- Number of atoms of hydrogen (H): 2
- Atomic mass of hydrogen (H): 1.008
- Number of atoms of oxygen (O): 1
- Atomic mass of oxygen (O): 15.999
Molar mass of water (H2O):
Molar mass = (2 x 1.008) + (1 x 15.999) = 18.015 g/mol
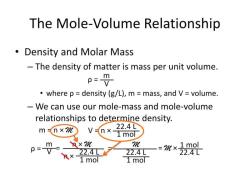
Detailing the formula for determining the molar mass of a substance and its significance
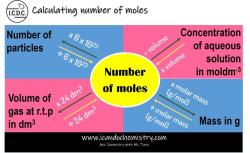
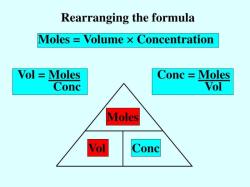
The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance. A mole is a unit of measurement that is equal to 6.022 x 10^23 particles, such as atoms, molecules, or ions.
Molar mass is a significant concept in chemistry because it allows us to convert between the mass and moles of a substance. This is useful for many calculations, such as balancing chemical equations, determining the amount of reactants needed for a reaction, and calculating the theoretical yield of a reaction.
Tips for students and researchers in calculating and applying molar mass in chemistry
Here are some tips for students and researchers in calculating and applying molar mass in chemistry:
- Make sure to use the correct atomic masses for the elements in your calculation. You can find the atomic masses on the periodic table.
- Be careful with the subscripts in chemical formulas. The subscript tells you how many atoms of each element are in the molecule.
- If you are calculating the molar mass of a compound, make sure to multiply the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms of that element in the compound.
- Molar mass is often used in chemical calculations, so it is important to be able to calculate it accurately.
Here are some examples of how molar mass can be applied in chemistry:
- Balancing chemical equations: Molar mass can be used to balance chemical equations by making sure that the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products.
- Determining the amount of reactants needed for a reaction: Molar mass can be used to determine the amount of reactants needed for a reaction by using the mole ratio from the balanced chemical equation.
- Calculating the theoretical yield of a reaction: Molar mass can be used to calculate the theoretical yield of a reaction by multiplying the moles of the limiting reactant by the molar mass of the desired product.
Molar mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and it is important for students and researchers to be able to calculate and apply it accurately.