How to find volume using moles?
To find the volume using moles, you can use the ideal gas law, which is often applicable to gases under certain conditions. The ideal gas law is given by the equation:
where:
- is the pressure of the gas,
- is the volume of the gas,
- is the number of moles of the gas,
- is the ideal gas constant, and
- is the temperature of the gas in kelvin.
If you know the values of three of the variables in the equation, you can rearrange the equation to solve for the fourth variable. To find the volume (), you rearrange the ideal gas law as follows:
Here's how you can use this formula:
Convert Temperature to Kelvin:
- Ensure that the temperature is in kelvin. If it's given in Celsius, add 273.15 to convert to kelvin.
Plug in Values:
- Plug in the values for the other variables into the equation. Make sure to use consistent units.
- is the number of moles,
- is the ideal gas constant (approximately 0.0821 L⋅atm/(mol⋅K)),
- is the temperature in kelvin, and
- is the pressure.
Solve for Volume:
- Perform the calculations to find the volume ().
Example:
Suppose you have 2 moles of a gas at a temperature of 300 K and a pressure of 1 atm. Using the ideal gas law, you can find the volume:
V = \frac{{(2 \, \text{{mol}}) \times (0.0821 \, \text{{L⋅atm/(mol⋅K)}}) \times (300 \, \text{{K})}}{{1 \, \text{{atm}}}}
So, in this example, the volume of the gas would be approximately 49.26 liters.
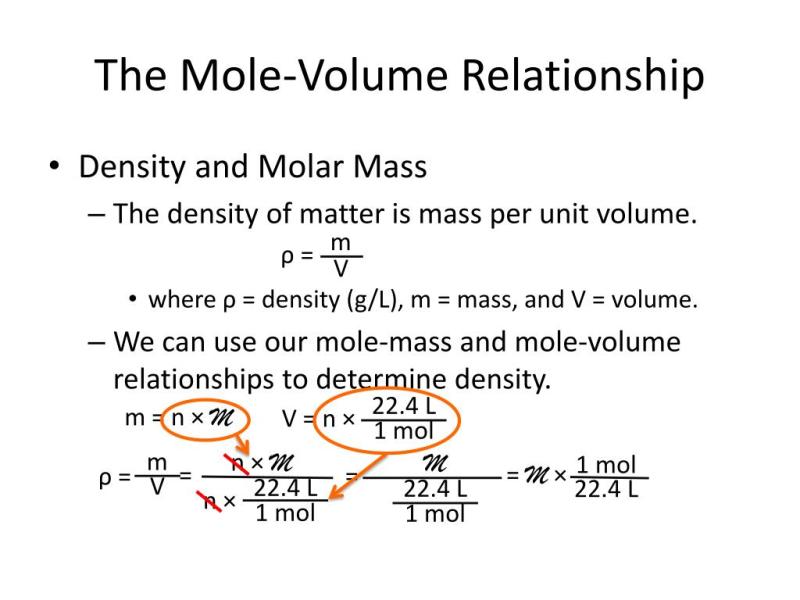
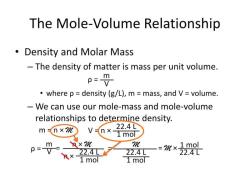
1. Understanding the Concept of Molar Volume
Molar volume, denoted by the symbol Vm, is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance at a specific temperature and pressure. It is a fundamental concept in chemistry that allows us to relate the number of moles of a substance to its volume.
The molar volume of a substance is inversely proportional to its molar mass, which is the mass of one mole of the substance. This relationship can be expressed by the following formula:
Vm = (1 dm^3/mol) / (Molar Mass)
where:
- Vm is the molar volume in cubic decimeters per mole (dm^3/mol)
- Molar Mass is the molar mass in grams per mole (g/mol)
At standard temperature and pressure (STP), defined as 0 degrees Celsius (273.15 Kelvin) and 1 atmosphere pressure, the molar volume of all gases is approximately 22.4 liters per mole (L/mol). This means that one mole of any gas at STP occupies a volume of 22.4 liters.
2. Applying the Molar Volume Formula
The molar volume formula is used to calculate the volume of a substance given its number of moles and molar mass. The formula can be rearranged to solve for the number of moles or molar mass as well.
Here's an example of how to use the molar volume formula to calculate the volume of 0.5 moles of helium (He) at STP:
Vm = (1 dm^3/mol) / (Molar Mass)
Given:
- Vm = 22.4 L/mol (molar volume of helium at STP)
- Molar Mass = 4.003 g/mol (molar mass of helium)
Calculation:
Volume = Vm * Number of moles
Volume = 22.4 L/mol * 0.5 moles
Volume = 11.2 L
Therefore, 0.5 moles of helium at STP occupies a volume of 11.2 liters.
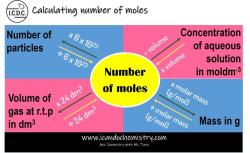
3. Solving Volume-Related Problems Using Moles
The molar volume relationship can be used to solve a variety of volume-related problems in chemistry. Here are some examples:
Calculating the volume of a gas mixture: Use the molar volume formula to calculate the volume of each gas in the mixture separately and then add the volumes together.
Determining the density of a gas: Density is defined as mass per unit volume. Use the molar volume formula to calculate the volume of the gas and then divide its mass by the volume to find the density.
Converting between gas volumes at different temperatures and pressures: Use the ideal gas law to relate the volume, temperature, and pressure of a gas.