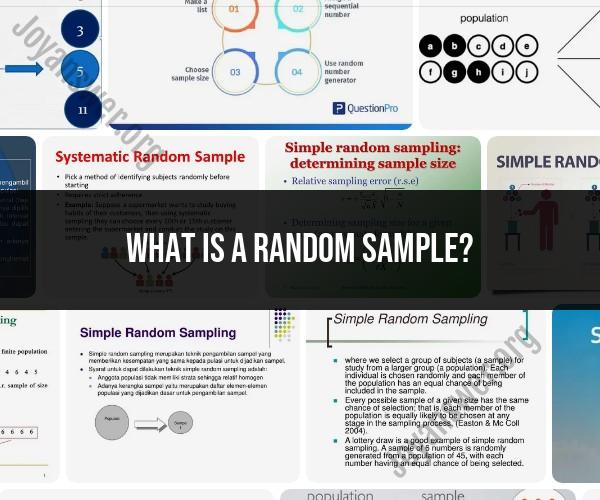
What is a random sample?
A random sample is a subset of individuals or items selected from a larger population in such a way that each member of the population has an equal and independent chance of being included in the sample. The process of selecting a random sample is a fundamental concept in statistics and plays a crucial role in making inferences about a population based on the characteristics observed in the sample.
Here are some key characteristics and principles associated with random sampling:
Randomness: The most crucial aspect of a random sample is that it is selected randomly, meaning that every individual or item in the population has an equal chance of being chosen. This randomness helps to avoid bias in the selection process.
Independence: Each selection in the sample is independent of the others. This means that the inclusion or exclusion of one individual/item does not affect the probability of including any other individual/item.
Representativeness: A good random sample should be representative of the population from which it is drawn. In other words, the characteristics of the sample should mirror those of the entire population as closely as possible. This ensures that inferences made from the sample can be generalized to the entire population.
Sampling Methods: There are various methods to obtain a random sample, including simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and systematic sampling. The choice of method depends on the research objectives and the characteristics of the population.
Simple Random Sampling: Involves randomly selecting individuals/items from the population without any specific criteria. It can be done with or without replacement (where a selected individual/item is or isn't returned to the population before the next selection).
Stratified Sampling: Divides the population into subgroups (strata) based on certain characteristics and then takes random samples from each stratum. This is useful when you want to ensure representation of different subgroups in your sample.
Cluster Sampling: Divides the population into clusters or groups and then randomly selects a subset of clusters. All individuals/items within the selected clusters are included in the sample. This method is useful when it's difficult to sample from the entire population directly.
Systematic Sampling: Involves selecting every nth individual/item from a list or sequence after randomly choosing a starting point.
Random sampling is essential in statistical research because it allows researchers to make inferences about the population based on the characteristics observed in the sample. When done correctly, it helps ensure that the sample is not biased and that the results can be generalized with a known degree of statistical confidence to the entire population. However, non-random or biased sampling methods can lead to misleading or inaccurate conclusions.