What is an example of a discrete variable?
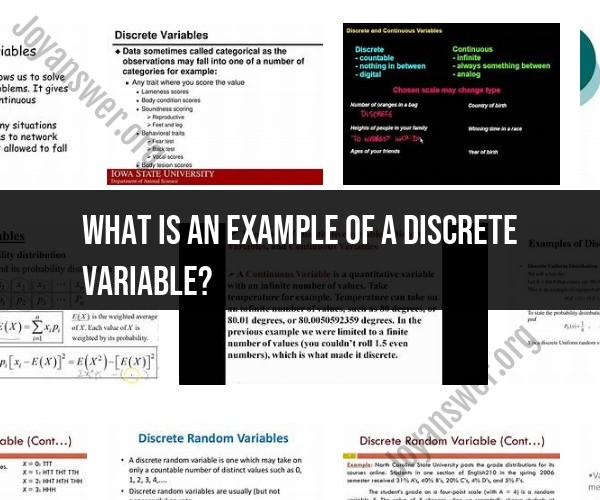
Discrete variables are a fundamental concept in statistics and data analysis. Let's delve into what discrete variables are, explore some examples, and gain a clear understanding of their significance.
Definition of Discrete Variables:
A discrete variable is a type of quantitative variable that takes on distinct, separate values. These values are typically counted and are often whole numbers. Discrete variables are characterized by gaps between possible values, and they cannot take on values in between these specific points.
Examples of Discrete Variables:
1. Number of Children in a Family:
The number of children in a family is a discrete variable. It can take on integer values, such as 0, 1, 2, 3, etc. There are clear gaps between these values, and they are distinct and separate.
2. Number of Cars in a Parking Lot:
The count of cars in a parking lot is another example of a discrete variable. It can only be a whole number, and there are distinct differences between the counts, with no values in between (e.g., 10 cars, 11 cars, 12 cars).
3. Dice Roll Outcome:
When rolling a six-sided die, the outcome is a discrete variable. The possible values are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. There are no values in between, and each roll results in a distinct and separate outcome.
4. Number of Pages in a Book:
The number of pages in a book is a discrete variable. Books have a specific count of pages, and there are no fractional or in-between values. The counts are distinct and separate from each other.
Significance of Discrete Variables:
Understanding discrete variables is crucial in statistical analysis, as they have unique properties that influence the way data is interpreted and analyzed. Discrete variables are essential for creating frequency distributions, calculating probabilities, and making informed decisions based on discrete values.
1. Frequency Distributions:
Discrete variables are used to create frequency distributions, which help visualize and analyze the distribution of data points. The distinct values of discrete variables allow for clear grouping and representation.
2. Probability Calculations:
Discrete variables are used in probability calculations, such as calculating the probability of a specific event occurring. The limited, separate values make it easier to determine the likelihood of outcomes.
3. Decision-Making:
Discrete variables play a role in decision-making processes that involve counts or distinct categories. For example, businesses may use discrete variables to analyze customer purchases or product quantities.
Conclusion:
Discrete variables are an integral part of statistical analysis, providing a framework for understanding and interpreting data with distinct and separate values. Recognizing these variables and their characteristics enables more accurate data analysis, probability calculations, and informed decision-making across various fields and industries.