How to find the temperature dependent viscosity and density?
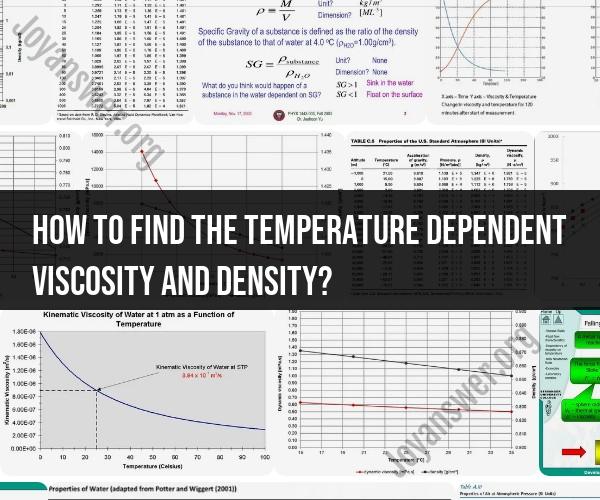
Viscosity and density are essential properties of fluids that play a significant role in various scientific and engineering applications. These properties often change with temperature, and understanding their temperature dependence is crucial for accurate predictions and calculations. In this guide, we'll explore how to determine the temperature-dependent viscosity and density of fluids.
Viscosity: A Brief Overview
Viscosity refers to a fluid's resistance to flow. It characterizes the internal friction within a fluid as it moves. Viscosity can vary significantly with temperature, affecting fluid behavior and flow patterns.
Methods for Determining Temperature-Dependent Viscosity
1. Empirical Correlations:
Empirical correlations are mathematical relationships derived from experimental data. These correlations provide an approximation of viscosity as a function of temperature. They are useful for obtaining quick estimates but may have limitations outside the specified temperature range.
2. Viscosity Tables:
Viscosity tables provide viscosity values at various temperatures for specific fluids. These tables are generated from experimental data and can be referenced for accurate viscosity values within their temperature ranges.
3. Viscosity Measurements:
Laboratory experiments involve directly measuring viscosity using viscometers or rheometers. These devices subject the fluid to controlled shear rates and measure its response. By conducting viscosity measurements at different temperatures, a viscosity-temperature relationship can be established.
Density: A Brief Overview
Density is the mass of a substance per unit volume. Like viscosity, density can also change with temperature due to changes in molecular arrangement and volume expansion or contraction.
Methods for Determining Temperature-Dependent Density
1. Equation of State:
Equations of state, such as the ideal gas law or the Peng-Robinson equation, describe the relationship between pressure, temperature, volume, and density for specific substances. These equations can provide density estimates at various temperatures.
2. Density Measurements:
Laboratory methods involve directly measuring density using instruments like densitometers or pycnometers. These devices determine the mass and volume of a sample to calculate density. Density measurements at different temperatures can help establish a density-temperature relationship.
3. Empirical Models:
Similar to viscosity, empirical models based on experimental data can provide approximations of density as a function of temperature. These models are useful when experimental data is limited or unavailable.
Importance of Temperature-Dependent Data
Accurate viscosity and density data are crucial for a wide range of applications, including fluid dynamics, heat transfer, chemical processes, and material manufacturing. Understanding how these properties change with temperature allows engineers and scientists to make informed decisions and predictions.
Conclusion
Temperature-dependent viscosity and density are critical considerations in fluid-related studies and applications. Whether through empirical correlations, measurements, or equations of state, determining how these properties change with temperature ensures accurate results and enhances the understanding of fluid behavior under varying conditions.