What is the difference between a discrete and continuous variable?
Understanding the difference between discrete and continuous variables is fundamental in statistics and data analysis. These two types of variables play a crucial role in determining the nature of data and the appropriate analytical techniques to apply. Let's explore the distinction between discrete and continuous variables:
Discrete Variables:
Discrete variables are those that can only take on specific, distinct values. These values are often counted or whole numbers and cannot be subdivided further. Examples of discrete variables include the number of cars in a parking lot, the number of students in a class, or the number of goals scored in a soccer match.
Continuous Variables:
Continuous variables, on the other hand, can take on any value within a certain range. They are not limited to specific values and can be measured with great precision. Examples of continuous variables include height, weight, temperature, and time. These variables can be further divided into smaller intervals, allowing for more detailed analysis.
Key Differences:
- Discrete variables have distinct and separate values, while continuous variables have an infinite number of possible values within a range.
- Discrete variables are often represented by whole numbers, while continuous variables can include decimal values.
- Discrete variables are typically used for counting or measuring quantities, while continuous variables are used for measuring quantities that can change continuously.
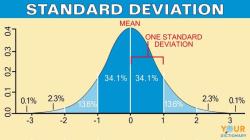
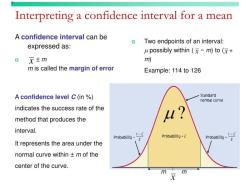
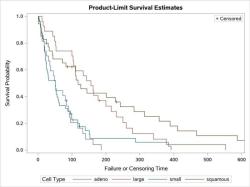
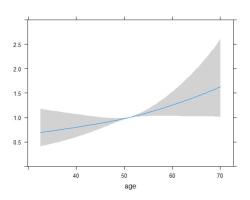
- Graphically, discrete variables are represented by individual data points, while continuous variables are depicted using smooth curves or lines.
Application:
The distinction between discrete and continuous variables is crucial in choosing the appropriate statistical methods. For discrete variables, techniques like bar charts and frequency distributions are commonly used. For continuous variables, histograms, scatter plots, and regression analysis are more applicable.
Conclusion:
Understanding the difference between discrete and continuous variables is fundamental in statistics and data analysis. Whether you're conducting research, analyzing data, or making informed decisions, recognizing the nature of the variables you're working with is essential for accurate interpretation and effective use of analytical methods.