How to merge DataFrames?
Merging DataFrames is a common operation when working with data in pandas, a popular data manipulation library in Python. It allows you to combine data from multiple DataFrames based on specified columns. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to merge DataFrames in pandas:
Import the Pandas Library
Before you start merging DataFrames, make sure you have the pandas library installed. You can import it into your Python script or Jupyter Notebook as follows:
import pandas as pd
DataFrames for Merging
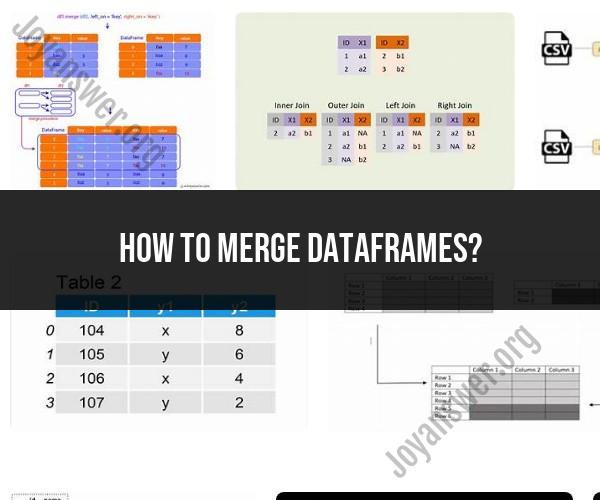
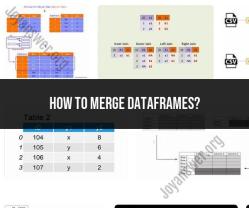
Assume you have two DataFrames, df1 and df2, and you want to merge them based on a common column.
Types of Merges
Pandas provides several types of merges, with the most common being the inner, outer, left, and right merge. The type of merge you choose depends on the data you want to retain from both DataFrames. Here are the main types:
- Inner Merge (Intersection): Retains only the rows that have matching keys in both DataFrames.
- Outer Merge (Union): Retains all rows from both DataFrames, filling in missing values with NaN where necessary.
- Left Merge: Retains all rows from the left DataFrame (
df1) and the matching rows from the right DataFrame (df2). - Right Merge: Retains all rows from the right DataFrame (
df2) and the matching rows from the left DataFrame (df1).
Merging DataFrames
To merge DataFrames, you typically use the pd.merge() function, which takes several arguments:
merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='type_of_merge', on='common_column')
df1anddf2are the DataFrames you want to merge.howspecifies the type of merge (inner, outer, left, or right).onis the common column on which the DataFrames are merged.
Here are examples of each type of merge:
Inner Merge (Intersection):
merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='inner', on='common_column')
Outer Merge (Union):
pythonmerged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='outer', on='common_column')
Left Merge:
pythonmerged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='left', on='common_column')
Right Merge:
merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='right', on='common_column')
Additional Merge Options
Left and Right DataFrames with Different Column Names: If the common column in
df1anddf2has different names, you can specify them explicitly:merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='type_of_merge', left_on='column_df1', right_on='column_df2')Merging on Multiple Columns: You can merge on multiple columns by passing a list of column names to the
onparameter:merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='type_of_merge', on=['column1', 'column2'])Handling Non-Matching Rows: If you want to handle non-matching rows more explicitly, you can use the
indicatorparameter to create a special column indicating the source of each row (left, right, or both).merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='type_of_merge', on='common_column', indicator=True)Custom Suffixes: When your DataFrames have columns with the same names, you can specify custom suffixes for the overlapping columns using the
suffixesparameter.merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='type_of_merge', on='common_column', suffixes=('_left', '_right'))Merging on Index: You can merge DataFrames on their indices using the
left_indexandright_indexparameters instead of theonparameter.merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, how='type_of_merge', left_index=True, right_index=True)
Merging DataFrames is a powerful way to combine and analyze data from multiple sources. Understanding the different types of merges and the options available in pandas allows you to tailor your data manipulation to your specific needs.
Merging DataFrames in Excel: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
To merge DataFrames in Excel, you can use the VLOOKUP function. The VLOOKUP function allows you to look up a value in one DataFrame and return a corresponding value from another DataFrame.
To merge DataFrames using VLOOKUP, follow these steps:
- Open the Excel spreadsheet that contains the two DataFrames that you want to merge.
- Select the cell where you want to put the first merged value.
- Type the following formula into the cell:
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
Where:
lookup_valueis the value in the first DataFrame that you want to use to look up the corresponding value in the second DataFrame.table_arrayis the range of cells in the second DataFrame that you want to search.col_index_numis the column number in the second DataFrame that contains the corresponding value that you want to return.range_lookupis an optional argument that specifies whether you want to use an exact match or approximate match.
- Press
Enter. - Copy the formula down the column to merge the rest of the DataFrames.
Combining Data from Multiple Sources Using Excel
You can use the VLOOKUP function to combine data from multiple sources using Excel. To do this, you would simply create a new DataFrame that contains the lookup values from all of the source DataFrames. Then, you would use the VLOOKUP function to look up the corresponding values from each of the source DataFrames and return them to the new DataFrame.
For example, suppose you have two DataFrames, one that contains customer names and email addresses and another that contains customer names and phone numbers. You could create a new DataFrame that contains the customer names from both DataFrames. Then, you could use the VLOOKUP function to look up the corresponding email addresses and phone numbers from each of the source DataFrames and return them to the new DataFrame.
Advanced Techniques for Merging DataFrames Efficiently
There are a number of advanced techniques that you can use to merge DataFrames efficiently in Excel. One technique is to use the Power Query add-in. Power Query is a powerful tool that allows you to clean, transform, and merge data.
To merge DataFrames using Power Query, follow these steps:
- Open the Excel spreadsheet that contains the two DataFrames that you want to merge.
- Click the Data tab.
- In the Get & Transform Data group, click Get Data from Other Sources > From Excel Files.
- Select the Excel file that contains the first DataFrame that you want to merge.
- Click Open.
- Power Query will open a new window.
- In the Power Query Editor, select the Transform tab.
- In the Merge Queries group, click Merge Queries.
- In the Merge Queries dialog box, select the second DataFrame that you want to merge.
- Click OK.
- Power Query will merge the two DataFrames and return a new DataFrame.
- Click Close & Apply to close the Power Query Editor and return to Excel.
Another technique for merging DataFrames efficiently is to use the pandas library in Python. Pandas is a powerful library for data analysis in Python.
To merge DataFrames using pandas, follow these steps:
- Import the
pandaslibrary. - Read the two DataFrames into
pandasDataFrames. - Use the
merge()function to merge the two DataFrames. - Write the merged DataFrame to Excel.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Data Merge Operations
There are a number of common issues that can occur when merging DataFrames. One common issue is that the DataFrames may not contain the same columns. To resolve this issue, you can use the pandas.merge.merge() function with the how parameter set to outer. This will merge the DataFrames even if they do not contain the same columns.
Another common issue is that the DataFrames may contain different data types for the same column. To resolve this issue, you can use the pandas.to_numeric() function to convert all of the values in the column to numerics.
Practical Applications of DataFrame Merging in Spreadsheet Management
DataFrame merging is a powerful tool that can be used for a variety of tasks in spreadsheet management. Here are a few examples:
- Combining data from multiple sources: DataFrame merging can be used to combine data from multiple sources