What should a data analyst know?
Data analysts play a crucial role in extracting meaningful insights from data to inform business decisions. Here is a list of essential knowledge areas for data analysts:
Statistical Analysis and Mathematics:
- Descriptive statistics (mean, median, mode, variance, standard deviation).
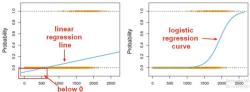
- Inferential statistics (hypothesis testing, regression analysis).
- Probability theory.
Programming Skills:
- Proficiency in languages such as Python, R, or SQL.
- Data manipulation and analysis using libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and scikit-learn (in Python).
Data Cleaning and Preprocessing:
- Identifying and handling missing data.
- Dealing with outliers.
- Data normalization and scaling.
Data Visualization:
- Creating meaningful visualizations using tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn (in Python), or ggplot2 (in R).
- Interpretation of charts and graphs.
Database Knowledge:
- SQL for querying relational databases.
- Understanding of database structures and relationships.
Machine Learning Basics:
- Understanding of machine learning algorithms and their applications.
- Knowledge of supervised and unsupervised learning.
Excel Proficiency:
- Advanced Excel skills for data manipulation and analysis.
- Pivot tables, charts, and formulas.
Business Acumen:
- Understanding of the business context and goals.
- Ability to translate data insights into actionable recommendations.
Communication Skills:
- Effective communication of data findings to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Creating clear and concise reports.
Problem-Solving Skills:
- Ability to identify and define problems.
- Developing analytical approaches to problem-solving.
Data Governance and Ethics:
- Understanding of data privacy and ethical considerations.
- Knowledge of data governance principles.
Tools for Data Analysis:
- Familiarity with tools such as Jupyter Notebooks, Tableau, or Power BI.
- Version control systems like Git.
Time Management:
- Efficiently managing time and prioritizing tasks.
- Meeting deadlines for analysis and reporting.
Continuous Learning:
- Staying updated on the latest trends and technologies in data analytics.
- Pursuing additional training or certifications as needed.
Domain Knowledge:
- Understanding of the specific industry or domain in which the data analysis is being performed.
- Knowledge of relevant key performance indicators (KPIs).
Collaboration Skills:
- Working effectively in a team.
- Collaborating with data scientists, engineers, and business stakeholders.
Remember that the specific requirements may vary depending on the industry and the organization. Data analysts often need to adapt and acquire new skills as technology and analytical methods evolve. Continuous learning and a willingness to explore new tools and techniques are essential for a successful career in data analysis.
- Knowledge Areas for Data Analysts
Data analysts should possess a broad knowledge base in various areas to effectively collect, analyze, and interpret data. These knowledge areas typically include:
Statistics: A strong foundation in statistics is essential for data analysts to understand data variability, probability distributions, hypothesis testing, and regression analysis.
Mathematics: Data analysts often utilize mathematical concepts such as calculus, linear algebra, and probability theory to perform advanced data analysis and modeling.
Computer Science: Familiarity with programming languages like Python, R, and SQL is crucial for data analysts to extract, manipulate, and process data from various sources.
Data Warehousing and Databases: Understanding data warehousing principles and database management systems (DBMS) enables data analysts to organize, store, and retrieve data efficiently.
Domain Knowledge: Depending on the specific industry or application area, data analysts may need to acquire specialized knowledge of the relevant domain to interpret data meaningfully and provide context-specific insights.
- Essential Skills and Competencies for Data Analysts
Data analysts require a combination of technical and soft skills to succeed in their roles. These skills include:
Problem-solving and Analytical Thinking: Data analysts must be able to identify problems, formulate insightful questions, and analyze complex datasets to extract meaningful insights.
Communication and Storytelling: Data analysts should effectively communicate their findings to both technical and non-technical audiences, translating data into clear and actionable insights.
Data Visualization: Creating compelling data visualizations is crucial for communicating complex data patterns, trends, and relationships in a visually appealing and understandable manner.
Attention to Detail and Accuracy: Data analysts must be meticulous and detail-oriented to ensure the accuracy and integrity of their data analysis and reporting.
Adaptability and Continuous Learning: The data landscape is constantly evolving, and data analysts need to be adaptable and have a willingness to learn new techniques and tools to stay relevant.
- Crucial Expertise for a Successful Data Analyst Career
Beyond the fundamental knowledge and skills, certain areas of expertise can further enhance a data analyst's career prospects and open up opportunities for specialization:
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI): As AI and machine learning become increasingly prevalent, data analysts with expertise in these areas can develop predictive models, automate data analysis tasks, and gain a competitive edge.
Big Data and Cloud Computing: With the growing volume and complexity of data, proficiency in big data technologies and cloud-based data platforms is becoming increasingly valuable for data analysts.
Business Acumen and Industry Expertise: Data analysts who can demonstrate an understanding of business processes and industry-specific challenges are more likely to provide actionable insights that directly impact business goals.
Collaboration and Teamwork: Data analysts often work collaboratively with stakeholders from various departments and expertise, requiring strong communication, interpersonal, and teamwork skills.