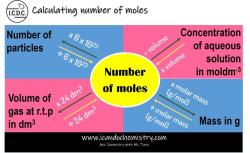
What is the formula for moles in chemistry?
The formula for calculating the number of moles in chemistry is:
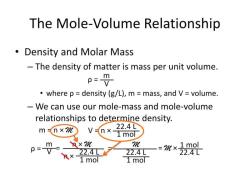
Number of Moles (n) = Mass (m) / Molar Mass (M)
Where:
- Number of Moles (n) is the quantity of substance measured in moles.
- Mass (m) is the mass of the substance in grams.
- Molar Mass (M) is the molar mass of the substance, which is typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). It represents the mass of one mole of atoms, molecules, or ions of the substance.
This formula is a fundamental concept in chemistry and is often used in various calculations, including determining the amount of reactants and products in chemical reactions, converting between mass and moles, and more. It's based on Avogadro's number, which tells us that one mole of any substance contains approximately 6.022 x 10^23 representative particles (atoms, molecules, or ions).
Moles in Chemistry: Understanding the Fundamental Formula
The mole is a fundamental unit of measurement in chemistry. It is defined as the amount of substance that contains the same number of elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12. The number of elementary entities in a mole is known as the Avogadro constant, which is approximately 6.022 × 1023.
The mole formula is a simple equation that allows you to calculate the number of moles in a given mass of a substance. The formula is as follows:
n = m / M
where:
- n is the number of moles
- m is the mass of the substance in grams
- M is the molar mass of the substance in grams per mole
The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance. It can be calculated by adding up the atomic masses of all the atoms in the substance. For example, the molar mass of water (H2O) is 18.02 grams per mole, because one mole of water contains two moles of hydrogen (H), each with an atomic mass of 1.008 grams per mole, and one mole of oxygen (O), with an atomic mass of 15.999 grams per mole.
The Mole Formula Demystified: A Chemistry Basics Guide
Here is an example of how to use the mole formula to calculate the number of moles in a given mass of a substance:
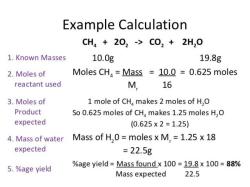
Problem: How many moles of sodium chloride (NaCl) are in 10.0 grams of NaCl?
Solution:
- Determine the molar mass of NaCl:
M = 22.99 + 35.45 = 58.44 grams per mole
- Substitute the known values into the mole formula:
n = m / M = 10.0 grams / 58.44 grams per mole = 0.171 moles
Therefore, there are 0.171 moles of NaCl in 10.0 grams of NaCl.
Counting Atoms: The Formula for Calculating Moles in Chemistry
The mole formula can also be used to calculate the number of atoms in a given mass of a substance. To do this, simply multiply the number of moles by the Avogadro constant.
For example, to calculate the number of atoms in 10.0 grams of NaCl, we would first calculate the number of moles of NaCl, as shown above. Once we know the number of moles, we can multiply it by the Avogadro constant to get the number of atoms:
Number of atoms = n * Avogadro constant = 0.171 moles * 6.022 × 1023 atoms per mole = 1.03 × 1023 atoms
Therefore, there are 1.03 × 1023 atoms in 10.0 grams of NaCl.
The mole formula is a powerful tool that can be used to calculate a variety of quantities in chemistry, including the number of moles, atoms, and molecules in a given mass of a substance.