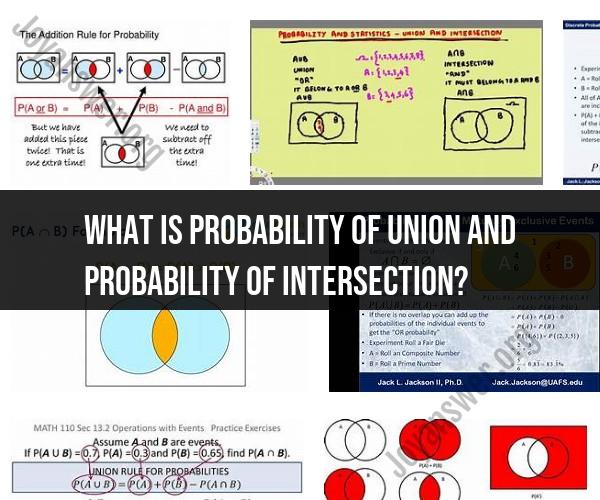
What is probability of Union and probability of intersection?
In probability theory and set theory, the probability of union and the probability of intersection are two fundamental concepts that describe the likelihood of events occurring in a sample space. These concepts are often denoted as P(A ∪ B) for the probability of union and P(A ∩ B) for the probability of intersection. Here's what they mean:
Probability of Union (P(A ∪ B)):
The probability of union, denoted as P(A ∪ B), represents the likelihood that at least one of two events, A or B, will occur.
Mathematically, P(A ∪ B) is calculated as the sum of the probabilities of A and B minus the probability of their intersection:
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∩ B)
The probability of union considers the combined probability of events A and B occurring individually and any overlap between them (the intersection).
Probability of Intersection (P(A ∩ B)):
The probability of intersection, denoted as P(A ∩ B), represents the likelihood that both events A and B will occur simultaneously.
Mathematically, P(A ∩ B) is simply the probability of both events occurring together.
The probability of intersection considers the shared outcomes between events A and B.
Here are a few important points to note:
P(A ∪ B) is always equal to or greater than the maximum of P(A) and P(B). This is because the union of events A and B includes all the outcomes from either event A, event B, or both.
P(A ∩ B) is equal to or less than the minimum of P(A) and P(B). This is because the intersection of events A and B only includes outcomes that satisfy both event A and event B.
When events A and B are mutually exclusive (i.e., they cannot occur simultaneously), then P(A ∩ B) = 0, and P(A ∪ B) simplifies to P(A) + P(B), which represents the probability of either event A or event B occurring.
The inclusion-exclusion principle, as shown in the formula for P(A ∪ B), allows us to account for overlapping outcomes when calculating the probability of the union of two events.
These concepts are fundamental in probability calculations, especially when dealing with multiple events or situations where events can either overlap or be independent of each other. Probability of union and probability of intersection play a crucial role in various branches of mathematics, statistics, and real-world applications like statistics, finance, and data science.
Understanding Probability: Exploring the Concepts of Union and Intersection
Probability is the measure of how likely an event is to occur. It is expressed as a number between 0 and 1, where 0 means that the event is impossible and 1 means that the event is certain.
The union of two events A and B is the event that either A or B or both A and B occur. The intersection of two events A and B is the event that both A and B occur.
Probability of Union vs. Probability of Intersection: Key Differences
The probability of the union of two events is always greater than or equal to the probability of the intersection of the two events. This is because the union of two events includes all of the outcomes that are included in the intersection of the two events, plus any additional outcomes that are included in either A or B but not both.
Another key difference between the probability of union and the probability of intersection is that the probability of union can be greater than 1, while the probability of intersection can never be greater than 1. This is because the probability of union is the sum of the probabilities of the individual events, and the sum of two numbers can be greater than 1.
Calculating Probabilities: The Mathematics Behind Union and Intersection
The probability of the union of two events A and B can be calculated using the following formula:
P(A U B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∩ B)
where P(A) is the probability of event A, P(B) is the probability of event B, and P(A ∩ B) is the probability of the intersection of events A and B.
The probability of the intersection of two events A and B can be calculated using the following formula:
P(A ∩ B) = P(A) * P(B)
where P(A) is the probability of event A and P(B) is the probability of event B.
Examples
Here are some examples of how to calculate the probabilities of union and intersection:
- Example 1: Flipping a coin twice.
The probability of flipping a coin and getting heads is 1/2. The probability of flipping a coin and getting tails is also 1/2. The probability of flipping a coin and getting either heads or tails is therefore 1/2 + 1/2 = 1. This is because the union of the two events "flipping a coin and getting heads" and "flipping a coin and getting tails" includes all of the possible outcomes.
- Example 2: Rolling a die.
The probability of rolling a die and getting a 6 is 1/6. The probability of rolling a die and getting a 5 is also 1/6. The probability of rolling a die and getting either a 5 or a 6 is therefore 1/6 + 1/6 = 1/3. This is because the union of the two events "rolling a die and getting a 5" and "rolling a die and getting a 6" includes all of the possible outcomes.
- Example 3: Drawing a card from a deck.
The probability of drawing a heart from a deck of 52 cards is 13/52. The probability of drawing a spade from a deck of 52 cards is also 13/52. The probability of drawing either a heart or a spade from a deck of 52 cards is therefore 13/52 + 13/52 = 26/52 = 1/2. This is because the union of the two events "drawing a heart from a deck of 52 cards" and "drawing a spade from a deck of 52 cards" includes all of the possible outcomes.
Conclusion
The concepts of union and intersection are important in probability because they allow us to calculate the probabilities of events that involve multiple outcomes. By understanding the key differences between the probability of union and the probability of intersection, and by knowing how to calculate these probabilities, we can better understand the world around us and make more informed decisions.