How to find molarity equation?
The molarity (M) of a solution is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a given volume of the solution. It is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. The formula for calculating molarity is:
In this formula:
- "Moles of Solute" is the amount of solute (in moles) that is dissolved or present in the solution.
- "Volume of Solution" is the total volume of the solution, including both the solvent and the solute, and it is measured in liters.
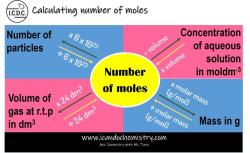
To find the molarity equation, you need to rearrange the formula to solve for one of the variables if you have the values of the other two variables. Here are some common variations of the molarity equation:
Finding Moles of Solute (n):
If you know the molarity (M) and the volume of the solution (V), you can find the moles of solute (n) using this equation:
Finding Volume of Solution (V):
If you know the moles of solute (n) and the molarity (M), you can find the volume of the solution (V) using this equation:
Finding Molarity (M):
If you know the moles of solute (n) and the volume of the solution (V), you can find the molarity (M) using this equation:
These equations are interchangeable and can be used to solve for any of the three variables (moles of solute, volume of solution, or molarity) if you have values for the other two. They are fundamental tools in chemistry for calculating concentrations of solutions and are often used in laboratory work and chemical calculations.
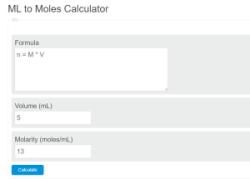
Example: Calculating Molarity
Suppose you have 0.25 moles of potassium chloride (KCl) dissolved in 500 milliliters (0.5 liters) of water to make a solution. Calculate the molarity (M) of the solution.
Gather Information:
- Moles of KCl = 0.25 moles
- Volume of solution = 0.5 liters
Plug Values into the Molarity Equation:
Perform the Calculation:
Express the Result:
The molarity of the solution is 0.5 M (0.5 moles per liter).
So, in this example, the molarity of the solution containing 0.25 moles of KCl dissolved in 0.5 liters of water is 0.5 M. This means there are 0.5 moles of KCl in each liter of the solution.