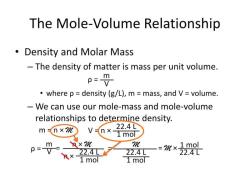
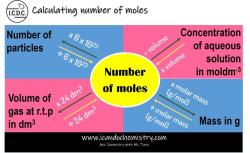
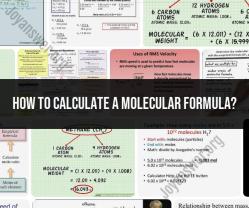
How to calculate moles from molecular weight?
To calculate moles from molecular weight, you can use the following formula:
In mathematical terms:
where:
- is the number of moles.
- is the mass of the substance in grams.
- is the molecular weight (also known as molar mass) of the substance in grams per mole.
Here are the steps to calculate moles from molecular weight:
Determine the Mass (m):
- Find the mass of the substance in grams. This is the amount of the material you have.
Identify the Molecular Weight (M):
- Determine the molecular weight of the substance. You can find this information on the periodic table or by adding up the atomic weights of all the atoms in a molecule.
Apply the Formula:
- Plug the mass (m) and molecular weight (M) into the formula .
Perform the Calculation:
- Divide the mass by the molecular weight to obtain the number of moles.
Here's an example:
Suppose you have 60 grams of glucose (C6H12O6), and you want to calculate the number of moles.
Determine the Mass (m):
Identify the Molecular Weight (M):
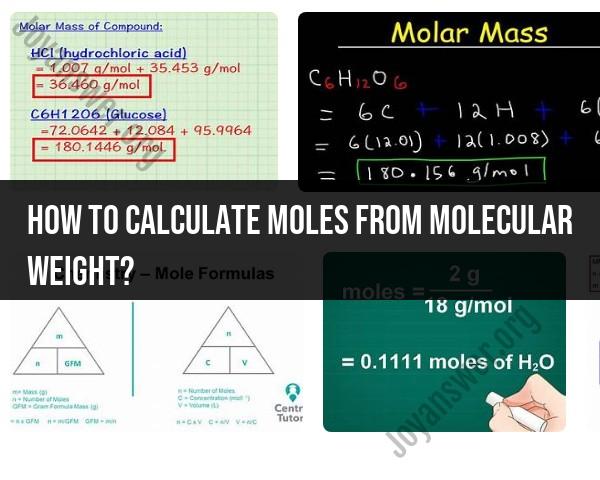
- Molecular weight of glucose (C6H12O6):
- Carbon (C): 12.01 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1.008 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
- Molecular weight of glucose (C6H12O6):
Apply the Formula:
Perform the Calculation:
So, in this example, you would have approximately 0.332 moles of glucose.
Ensure you use consistent units (grams for mass and grams per mole for molecular weight) to get accurate results.
Molecular weight calculation: How to calculate moles from molecular weight?
Molar mass, also known as molecular weight, is a fundamental concept in chemistry that relates the mass of a molecule to the number of atoms it contains. It is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). Moles, on the other hand, represent the amount of a substance in terms of the number of fundamental units, which can be atoms, molecules, or ions.
The conversion between molecular weight and moles involves a simple formula:
moles = mass (in grams) / molecular weight (in g/mol)
This formula essentially states that the number of moles is equal to the mass of the substance divided by its molecular weight.
Step-by-step guide to determining moles from molecular weight in chemistry
To determine the number of moles from molecular weight, follow these steps:
Identify the molecular formula of the substance. The molecular formula represents the arrangement and types of atoms in a molecule. For instance, the molecular formula for water is H2O, indicating two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in a molecule.
Calculate the molecular weight. The molecular weight of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in its molecular formula. You can find the atomic masses of elements on the periodic table. For example, the molecular weight of water (H2O) is:
Molecular weight = (2 × atomic mass of hydrogen) + atomic mass of oxygen
Molecular weight = (2 × 1.008 g/mol) + 15.9994 g/mol
Molecular weight ≈ 18.015 g/mol
Determine the mass of the substance. The mass is typically given in grams (g).
Apply the formula. Substitute the mass and molecular weight into the formula:
moles = mass (in grams) / molecular weight (in g/mol)
For example, to calculate the number of moles in 100 grams of water, you would use:
moles = 100 g / 18.015 g/mol ≈ 5.551 mol
Tips for students and chemists in molecular weight calculations
Here are some tips for students and chemists in molecular weight calculations:
Always use the correct units. Ensure that the mass is in grams (g) and the molecular weight is in grams per mole (g/mol).
Use the periodic table accurately. Refer to the periodic table to obtain the atomic masses of elements.
Be mindful of significant digits. Carry the correct number of significant digits throughout the calculation to maintain accuracy.
Double-check your work. Always review your calculations to ensure there are no errors.
Molecular weight calculations are essential for various chemical applications, including preparing solutions, balancing chemical equations, and determining the concentration of solutions. By following these steps and tips, you can perform molecular weight calculations accurately and confidently.