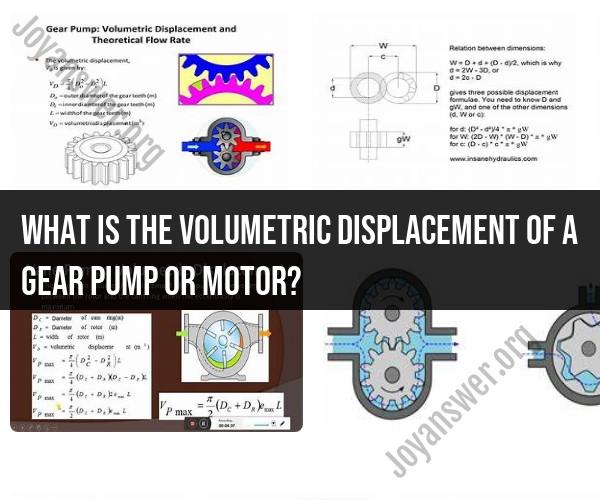
What is the volumetric displacement of a gear pump or motor?
The volumetric displacement of a gear pump or motor is a critical parameter in hydraulic systems. It refers to the volume of fluid that the pump or motor can move or displace per unit of time. This parameter is typically measured in cubic inches per revolution (in³/rev) or in milliliters per revolution (ml/rev) depending on the units used.
In the case of a gear pump, there are two main types: internal gear pumps and external gear pumps. Both types consist of two gears, one driving gear (the driver) and one driven gear (the idler), which mesh together and create a sealed chamber. As the gears rotate, they trap and move fluid from the inlet side to the outlet side. The volumetric displacement of a gear pump is determined by the size and geometry of the gears and the speed at which they rotate. It's typically a fixed displacement pump, meaning that it moves a consistent volume of fluid per revolution.
In the case of a gear motor, it operates in a similar manner to a gear pump but can also work in reverse. When hydraulic fluid is applied to the motor, it causes the gears to rotate, and the motor converts hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. The volumetric displacement of a gear motor is also determined by the size and geometry of the gears and the speed at which they rotate.
The formula for calculating the volumetric displacement of a gear pump or motor is:
Volumetric Displacement (in³/rev or ml/rev) = (π / 4) * (D^2 - d^2) * L
Where:
- π is the mathematical constant Pi (approximately 3.14159).
- D is the diameter of the driver gear (the larger gear).
- d is the diameter of the idler gear (the smaller gear).
- L is the width of the gear teeth.
The volumetric displacement is a fixed value for each specific pump or motor and is typically provided by the manufacturer in the product specifications. It is a crucial parameter when designing hydraulic systems because it determines the flow rate of the fluid in the system, which, in turn, affects the speed and force of hydraulic actuators.
Volumetric Displacement of Gear Pumps and Motors
Volumetric displacement is the volume of fluid that a gear pump or motor displaces per revolution. It is a measure of the pump or motor's size and capacity. The volumetric displacement of a gear pump or motor is calculated using the following equation:
Volumetric Displacement = (Gear Width) * (Gear Thickness) * (Pi * Gear Diameter)
where:
- Gear Width is the width of the gear face
- Gear Thickness is the thickness of the gear at the pitch circle
- Pi is the mathematical constant pi (3.14159)
- Gear Diameter is the diameter of the gear at the pitch circle
Calculating Volumetric Displacement in Hydraulic Systems
The volumetric displacement of a gear pump or motor is an important factor in hydraulic systems. The volumetric displacement of the pump must be equal to the volumetric displacement of the motor in order to maintain a constant flow rate in the system. If the pump's volumetric displacement is greater than the motor's volumetric displacement, the system will experience overpressure. If the pump's volumetric displacement is less than the motor's volumetric displacement, the system will experience cavitation.
Importance of Volumetric Displacement in Gear Pumps
The volumetric displacement of a gear pump is an important factor in determining its operating characteristics and performance. The volumetric displacement of a gear pump affects the following factors:
- Flow rate: The volumetric displacement of a gear pump is directly proportional to its flow rate. A pump with a higher volumetric displacement will produce a higher flow rate.
- Pressure: The volumetric displacement of a gear pump is inversely proportional to its pressure capability. A pump with a higher volumetric displacement will produce a lower pressure.
- Speed: The volumetric displacement of a gear pump determines its maximum speed. A pump with a higher volumetric displacement will have a lower maximum speed.
The volumetric displacement of a gear pump is also an important factor in selecting the correct pump for a particular application. The pump's volumetric displacement must be sized to meet the flow rate and pressure requirements of the application.
Here are some examples of how the volumetric displacement of a gear pump affects its performance:
- A gear pump with a high volumetric displacement will be able to pump more fluid per revolution, but it will produce a lower pressure. This type of pump is ideal for applications where high flow rates are required, such as hydraulic power units and industrial pumps.
- A gear pump with a low volumetric displacement will be able to produce a higher pressure, but it will pump less fluid per revolution. This type of pump is ideal for applications where high pressures are required, such as hydraulic presses and power steering pumps.
The volumetric displacement of a gear pump is a critical factor in determining its operating characteristics and performance. By understanding the importance of volumetric displacement, engineers can select the correct pump for their specific application.