How do you calculate the displacement of an engine?
Calculating the displacement of an engine is an important aspect of automotive engineering, as it provides a measure of the engine's size and capacity. Engine displacement, often expressed in liters (L) or cubic inches (CI), is a key factor in determining an engine's performance and efficiency. Displacement represents the total volume of all the engine's cylinders and is typically used as a basic measure of engine size.
To calculate engine displacement, follow these steps:
Determine the Engine's Cylinder Configuration:Engines come in various configurations, but the most common ones are inline, V, and flat (boxer) engines. You need to know how many cylinders the engine has and how they are arranged.
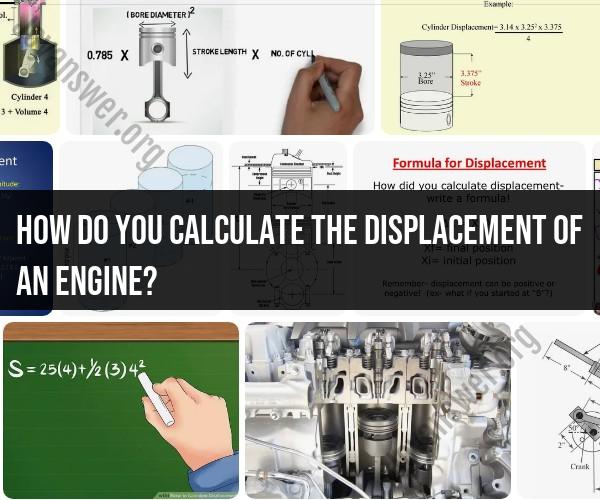
Measure the Bore and Stroke:The bore is the diameter of the cylinder, and the stroke is the distance the piston travels inside the cylinder during each cycle. These measurements are usually provided in millimeters (mm) or inches (in).
Calculate the Displacement of a Single Cylinder:Displacement for a single cylinder can be calculated using the formula for the volume of a cylinder:
Displacement of a Single Cylinder (in liters) = (π/4) × Bore² × Stroke / 1,000
The division by 1,000 is to convert the result to liters.
Determine the Total Number of Cylinders:Find out how many cylinders are in the engine. Most common automotive engines have 4, 6, or 8 cylinders, but there are engines with more or fewer cylinders.
Calculate the Total Displacement:To find the total engine displacement, multiply the displacement of a single cylinder by the number of cylinders:
Total Engine Displacement (in liters) = Displacement of a Single Cylinder (in liters) × Number of Cylinders
Convert the Units (if necessary):If the engine displacement was calculated in milliliters (ml) or cubic centimeters (cc), you can convert it to liters by dividing by 1,000.
Optionally, Convert to Cubic Inches:If you want the displacement in cubic inches, you can use the conversion factor: 1 liter is approximately equal to 61.02 cubic inches.
Here's an example of how to calculate the engine displacement:
Suppose you have a V8 engine with the following specifications:
- Bore: 90 mm
- Stroke: 75 mm
Calculate the Displacement of a Single Cylinder:Displacement of a Single Cylinder (in liters) = (π/4) × (90 mm)² × (75 mm) / 1,000 = 0.4967 liters
Determine the Total Number of Cylinders:V8 means eight cylinders.
Calculate the Total Engine Displacement:Total Engine Displacement (in liters) = 0.4967 liters (Single Cylinder Displacement) × 8 (Number of Cylinders) = 3.9736 liters
So, the engine has a total displacement of approximately 3.9736 liters or approximately 242 cubic inches.
Engine Displacement Calculation Methods
Engine displacement is a measure of the total volume of air and fuel that can be displaced by the pistons of an engine in a single revolution. It is one of the most important factors in determining the power and torque output of an engine.
There are two main methods for calculating engine displacement:
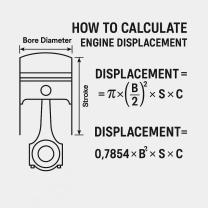
- Formula method: This method uses the following formula:
Displacement = (Bore^2 * Stroke * Pi * Number of cylinders) / 4
where:
- Bore is the diameter of the cylinder in inches or millimeters
- Stroke is the distance that the piston travels from top dead center (TDC) to bottom dead center (BDC) in inches or millimeters
- Pi is the mathematical constant pi (3.14159)
- Number of cylinders is the total number of cylinders in the engine
- Measurement method: This method involves measuring the actual volume of the combustion chambers in the engine. This can be done using a variety of methods, such as using a burette or a graduated cylinder.
Measuring Engine Displacement for Performance Analysis
Measuring engine displacement is important for performance analysis because it allows engineers to compare the size and capacity of different engines. It is also important for understanding the relationship between engine displacement and other performance factors, such as power, torque, and fuel economy.
To measure engine displacement for performance analysis, engineers typically use the measurement method described above. This method is more accurate than the formula method, especially for engines with complex combustion chamber designs.
Calculating the Displacement of an Internal Combustion Engine
To calculate the displacement of an internal combustion engine, you will need to know the bore, stroke, and number of cylinders of the engine. You can find this information in the engine's specifications or by measuring the bore and stroke yourself.
Once you have this information, you can use the following formula to calculate the displacement of the engine:
Displacement = (Bore^2 * Stroke * Pi * Number of cylinders) / 4
where:
- Bore is the diameter of the cylinder in inches or millimeters
- Stroke is the distance that the piston travels from TDC to BDC in inches or millimeters
- Pi is the mathematical constant pi (3.14159)
- Number of cylinders is the total number of cylinders in the engine
For example, if you have a 4-cylinder engine with a bore of 3.5 inches and a stroke of 3.8 inches, the displacement of the engine would be:
Displacement = (3.5^2 * 3.8 * Pi * 4) / 4 = 91.4 cubic inches
Engine displacement is an important factor to consider when choosing an engine for a particular application. A larger engine displacement will generally produce more power and torque, but it will also consume more fuel.