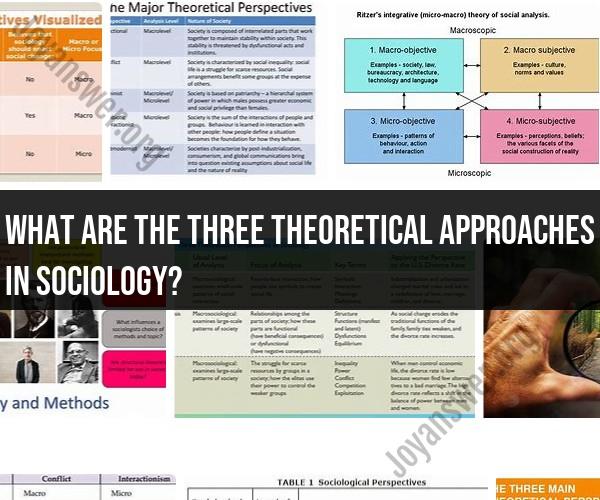
What are the three theoretical approaches in sociology?
The field of sociology encompasses various theoretical approaches and perspectives to understand and analyze society and social phenomena. Three key theoretical approaches in sociology are:
Structural-Functionalism:
- Structural-functionalism is a macro-level theory that views society as a complex system with various interrelated parts, each serving a specific function.
- It emphasizes the stability and order in society and suggests that social institutions and structures exist to fulfill essential functions for the overall functioning of society.
- Prominent figures associated with structural-functionalism include Emile Durkheim and Talcott Parsons.
Conflict Theory:
- Conflict theory, also a macro-level perspective, focuses on the power struggles and conflicts that exist within society.
- It argues that society is characterized by inequality and social stratification, with certain groups or classes having more power and resources than others.
- Conflict theorists, such as Karl Marx and Max Weber, analyze how these conflicts over resources and power shape social structures and institutions.
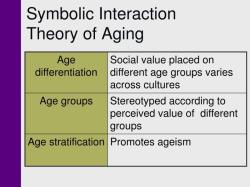
Symbolic Interactionism:
- Symbolic interactionism is a micro-level theory that examines the everyday interactions and symbols that individuals use to create and give meaning to their social reality.
- It emphasizes the role of symbols, language, and gestures in shaping social life, as well as the importance of individual agency and subjective meanings.
- Key figures associated with symbolic interactionism include George Herbert Mead and Erving Goffman.
These three theoretical approaches offer different perspectives for studying and understanding society, and sociologists often use a combination of these approaches to gain a comprehensive understanding of social phenomena. Additionally, there are other sociological perspectives and approaches, such as feminism, postmodernism, and critical theory, which provide alternative lenses for analyzing society and its dynamics.
Overview of Three Theoretical Approaches in Sociology
Sociology is the study of human society and social behavior. It is a broad discipline that encompasses a wide range of topics, including social institutions, culture, social stratification, inequality, and social change. Sociologists use a variety of theoretical perspectives to understand and explain social phenomena.
Three of the most well-known theoretical approaches in sociology are:
- Structural functionalism
- Conflict theory
- Symbolic interactionism
Structural functionalism views society as a system of interconnected parts, each of which plays a vital role in maintaining the stability and well-being of the whole. This approach focuses on the social functions of various institutions, such as the family, education system, and economy.
Conflict theory emphasizes the role of inequality and power struggles in shaping social life. It views society as being divided into competing groups, such as the rich and the poor, or the powerful and the powerless. Conflict theorists argue that these groups are constantly competing for resources and influence, and that this conflict is the driving force behind social change.
Symbolic interactionism focuses on the everyday interactions between people. It examines how people use symbols, such as language, gestures, and clothing, to communicate with each other and create shared meanings. Symbolic interactionists argue that these interactions are essential for understanding social reality.
These three theoretical approaches offer different but complementary perspectives on social life. Structural functionalism helps us to understand how society works as a system, conflict theory helps us to understand the role of inequality and power struggles in shaping society, and symbolic interactionism helps us to understand the importance of everyday interactions in creating social reality.
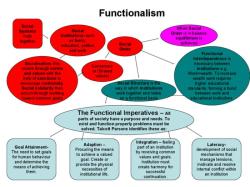
Key Concepts of Structural Functionalism in Sociology
Some of the key concepts of structural functionalism in sociology include:
- Social structure: Social structure refers to the patterns of relationships and social institutions that exist in a society. Structural functionalists argue that social structure is essential for social order and stability.
- Social functions: Social functions are the intended or unintended consequences of social structures and actions. Structural functionalists focus on the positive functions of social structures, such as how they contribute to the stability and well-being of society.
- Social equilibrium: Social equilibrium refers to a state of balance and stability in society. Structural functionalists argue that society is constantly striving to maintain social equilibrium.
Analyzing Conflict Theory in Sociological Perspectives
Some of the key concepts of conflict theory in sociology include:
- Social class: Social class refers to the system of stratification in a society that is based on socioeconomic status. Conflict theorists argue that social class is the most important factor in shaping social life and determining who gets what in society.
- Power: Power refers to the ability to influence or control others. Conflict theorists argue that power is unequally distributed in society and that this inequality leads to conflict and social change.
- Ideology: Ideology refers to the system of beliefs and ideas that justify the existing social order. Conflict theorists argue that ideology is used to maintain the power and privilege of the dominant class.
Conflict theory can be used to analyze a wide range of social phenomena, including:
- Crime and deviance: Conflict theorists argue that crime and deviance are often forms of resistance to the dominant social order.
- Education: Conflict theorists argue that the education system is used to reproduce social inequality and maintain the power and privilege of the dominant class.
- Gender: Conflict theorists argue that gender inequality is rooted in the unequal distribution of power between men and women.
Conflict theory is a valuable tool for understanding social life and the role of inequality and power struggles in shaping society. It offers a different perspective from structural functionalism, which focuses on the positive functions of social structures.
Conclusion
The three theoretical approaches in sociology discussed above offer different but complementary perspectives on social life. Structural functionalism helps us to understand how society works as a system, conflict theory helps us to understand the role of inequality and power struggles in shaping society, and symbolic interactionism helps us to understand the importance of everyday interactions in creating social reality.
Each of these theoretical approaches has its own strengths and weaknesses. Structural functionalism has been criticized for being too optimistic about the nature of society and for ignoring the role of conflict in social change. Conflict theory has been criticized for being too pessimistic about the nature of society and for ignoring the positive functions of social institutions. Symbolic interactionism has been criticized for being too narrow in its scope and for failing to account for larger social forces.
Despite these criticisms, all three of these theoretical approaches remain important tools for sociological analysis. They offer different but valuable perspectives on social life, and they can be used to understand a wide range of social phenomena.