How do you construct frequency distribution in Excel?
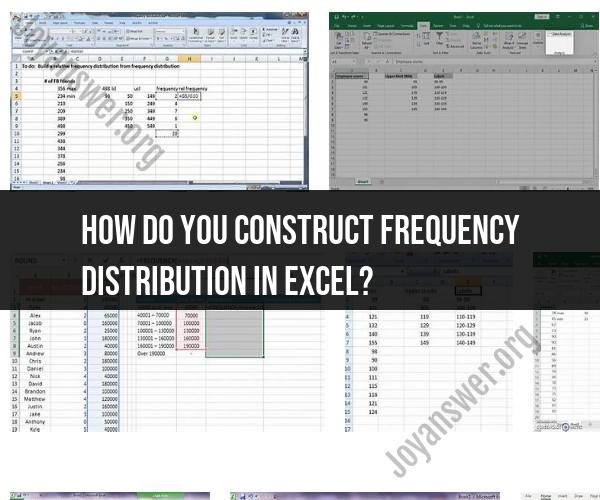
Constructing a frequency distribution in Excel involves organizing and counting data values into specific intervals or "bins" to show how often each value or range of values occurs in a dataset. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a frequency distribution in Excel:
Step 1: Organize Your Data
Ensure your data is well-organized in a column in Excel. This column should contain the data values you want to create a frequency distribution for. For example, if you're working with a dataset of test scores, the first column could contain the scores.
Step 2: Determine the Number of Bins (Intervals)
Decide on the number of intervals or "bins" you want to use for your frequency distribution. Bins group similar data values together. The number of bins depends on the range of your data and your preference for granularity. Common methods to determine the number of bins include the Sturges formula or Scott's rule, but you can also choose a meaningful number based on your data.
Step 3: Create a List of Bin Edges
Next, you need to create a list of bin edges or cutoff points for each interval. These values will define the boundaries of each bin. You can do this manually or use Excel's built-in functions to help. Here's how you can create bin edges:
- In a separate column, list the bin edges. For example, if you're creating bins for test scores and want to group scores into intervals of 10 (e.g., 0-9, 10-19, 20-29, etc.), you would list 0, 10, 20, 30, and so on in a column.
Step 4: Calculate Frequency Counts
Now, you'll use Excel functions to calculate the frequency count for each bin. Here's how to do it:
In another column next to your bin edges column, enter the following formula for the first bin (assuming your data starts in cell A2 and your bin edges are in column B):
=COUNTIFS(A2:A100,">="&B2,A2:A100,"<"&B3)- This formula counts the number of values in your data column (A2:A100) that are greater than or equal to the current bin edge (B2) and less than the next bin edge (B3).
Drag the fill handle (the small square at the bottom-right corner of the cell) down to copy the formula for all the bins.
Step 5: Create a Frequency Table
To make the frequency distribution more readable, create a table that includes both the bin edges and the corresponding frequency counts. You can add labels to your columns for clarity.
Step 6: Create a Histogram (Optional)
If you want to visualize the frequency distribution, you can create a histogram using Excel's charting capabilities. Here's how:
Select the frequency counts and bin edge columns (including labels) to highlight the data.
Go to the "Insert" tab and select a chart type like "Bar Chart" or "Column Chart."
Excel will create a histogram based on your data.
By following these steps, you can construct a frequency distribution in Excel and optionally visualize it with a histogram chart. This allows you to analyze the distribution of your data and gain insights into the frequency of different values or intervals.
Constructing Frequency Distributions in Excel: Step-by-Step Guide
To construct a frequency distribution in Excel, follow these steps:
- Enter your data in a column in Excel.
- Click on the Data tab and then click on the Data Analysis button.
- In the Data Analysis dialog box, select the Histogram option and click on the OK button.
- In the Histogram dialog box, select the Input range as the range of cells that contains your data.
- Select the Output range as the cell where you want the frequency distribution to be displayed.
- Click on the OK button.
Excel will create a frequency distribution table, which will show the number of times each value in your data set occurs.
Excel Frequency Distribution: Creating Data Breakdowns
A frequency distribution can be used to create data breakdowns that can be used to analyze your data and identify trends. For example, you could use a frequency distribution to break down your sales data by region, product, or customer segment.
To create a data breakdown using a frequency distribution, you can use the FREQUENCY function in Excel. The FREQUENCY function returns the number of times a value occurs in a given range of cells.
To use the FREQUENCY function, follow these steps:
- Enter the following formula in a cell:
=FREQUENCY(data_range, bin_range)
- data_range: The range of cells that contains your data.
- bin_range: The range of cells that contains the bins for your frequency distribution.
- Press Enter.
Excel will return the number of times each value in the data_range occurs in the corresponding bin in the bin_range.
Frequency Distribution Construction in Excel: Data Analysis
Frequency distributions can be used to perform a variety of data analysis tasks. For example, you could use a frequency distribution to:
- Identify the most common and least common values in your data set.
- Determine the central tendency of your data set (e.g., mean, median, and mode).
- Calculate the variability of your data set (e.g., variance and standard deviation).
- Identify trends in your data set.
To use frequency distributions for data analysis, you can use the following steps:
- Construct a frequency distribution for your data.
- Analyze the frequency distribution to identify patterns and trends.
- Use the information you have gathered from the frequency distribution to make decisions about your data.
Frequency distributions are a powerful tool that can be used to analyze data and identify trends. By following the steps above, you can construct and use frequency distributions to improve your understanding of your data and make better decisions.