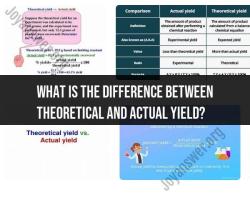
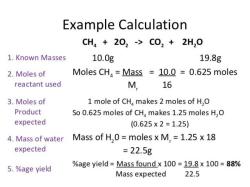
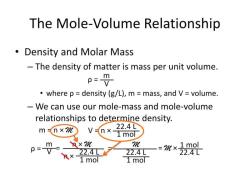
Is a conjugate of a weak acid a strong base?
No, the conjugate of a weak acid is not necessarily a strong base. The strength of a conjugate base depends on the specific weak acid in question and its equilibrium with water. The term "conjugate" in chemistry refers to a species that is related to another species by the gain or loss of a proton (H+).
Here's how it works:
Weak Acid and Its Conjugate Base:
- A weak acid is an acid that does not completely ionize (lose a proton) in an aqueous solution. When it donates a proton (H+), it forms its conjugate base.
- The conjugate base of a weak acid will typically be weak itself. This means it will not readily accept a proton (H+) from water and, therefore, will not be a strong base.
Example:
- Consider acetic acid (CH3COOH), which is a weak acid. When acetic acid donates a proton to water, it forms its conjugate base, acetate (CH3COO-).
- Acetate (CH3COO-) is the conjugate base of acetic acid, but it is also a weak base. It does not readily accept a proton from water to form hydroxide ions (OH-) and hydronium ions (H3O+), which are characteristic of strong bases.
In contrast, strong bases are substances that readily accept protons (H+) from water, leading to the production of hydroxide ions (OH-) and hydronium ions (H3O+). Strong bases are often ionic compounds like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH).
It's important to note that the strength of an acid or its conjugate base depends on its tendency to donate or accept protons in a solution. The strength of an acid does not necessarily dictate the strength of its conjugate base, and vice versa. Additionally, the strength of weak acids and their conjugate bases can vary widely depending on the specific chemical characteristics of the molecules involved.
No, the conjugate of a weak acid is not necessarily a strong base. The strength of a conjugate base depends on the specific weak acid in question and its equilibrium with water. The term "conjugate" in chemistry refers to a species that is related to another species by the gain or loss of a proton (H+).
Here's how it works:
Weak Acid and Its Conjugate Base:
- A weak acid is an acid that does not completely ionize (lose a proton) in an aqueous solution. When it donates a proton (H+), it forms its conjugate base.
- The conjugate base of a weak acid will typically be weak itself. This means it will not readily accept a proton (H+) from water and, therefore, will not be a strong base.
Example:
- Consider acetic acid (CH3COOH), which is a weak acid. When acetic acid donates a proton to water, it forms its conjugate base, acetate (CH3COO-).
- Acetate (CH3COO-) is the conjugate base of acetic acid, but it is also a weak base. It does not readily accept a proton from water to form hydroxide ions (OH-) and hydronium ions (H3O+), which are characteristic of strong bases.
In contrast, strong bases are substances that readily accept protons (H+) from water, leading to the production of hydroxide ions (OH-) and hydronium ions (H3O+). Strong bases are often ionic compounds like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH).
It's important to note that the strength of an acid or its conjugate base depends on its tendency to donate or accept protons in a solution. The strength of an acid does not necessarily dictate the strength of its conjugate base, and vice versa. Additionally, the strength of weak acids and their conjugate bases can vary widely depending on the specific chemical characteristics of the molecules involved.