How do I calculate random sampling?
Calculating random sampling involves selecting a subset of individuals or items from a larger population in a way that ensures each member of the population has an equal and independent chance of being chosen. Random sampling is a fundamental method in statistics and research to draw valid conclusions about a population based on a sample. Here are some common methods and considerations for calculating random sampling:
Simple Random Sampling:Simple random sampling is the most straightforward method for selecting a random sample. It involves assigning a unique number to each individual or item in the population and then using a random number generator or a random drawing method to select the desired number of samples.
Assign Numbers: Give each member of the population a unique number. If you're working with a list, you can number the list sequentially.
Random Selection: Use a random number generator or a random drawing method to select the desired number of samples. This ensures that each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
Stratified Random Sampling:Stratified random sampling involves dividing the population into subgroups (strata) based on certain characteristics and then randomly selecting samples from each stratum.
Identify Strata: Determine the characteristics that define strata within your population, such as age groups, geographic regions, or product categories.
Random Selection: Within each stratum, use simple random sampling to select samples. The size of each stratum should be proportional to its representation in the population.
Systematic Sampling:Systematic sampling involves selecting every nth member from the population. It can be an efficient method when the population is ordered, such as a list of students or items on a conveyor belt.
Define the Sampling Interval: Determine the sampling interval (e.g., every 5th member) based on the desired sample size and the population size.
Random Start: Choose a random starting point within the population to ensure randomness.
Select Samples: Start at the random starting point and select every nth member until you reach the desired sample size.
Cluster Sampling:Cluster sampling involves dividing the population into clusters and randomly selecting entire clusters to be part of the sample.
Define Clusters: Identify natural clusters within the population, such as households in a neighborhood or departments in a company.
Random Cluster Selection: Randomly select a predetermined number of clusters.
Sample Within Clusters: After selecting clusters, sample all members within those clusters.
Considerations:When calculating random sampling, consider the following:
Population Size: The size of the population will affect the sample size and the sampling method you choose.
Sample Size: Determine the desired sample size based on your research goals and statistical power requirements.
Sampling Frame: Ensure that your sampling frame (the list or source from which you select samples) is comprehensive and represents the entire population.
Randomness: The key to random sampling is ensuring that the selection process is truly random and free from bias. You may use random number generators, random drawing methods, or statistical software for this purpose.
Sampling Without Replacement: In most cases, each selected item should not be replaced in the population after being chosen to avoid duplication.
Random sampling is crucial for obtaining results that are representative of the entire population and for making valid statistical inferences. It helps minimize selection bias and improve the generalizability of your findings.
How to Calculate Random Sampling: Step-by-Step Guide
To calculate random sampling, follow these steps:
- Define the population. The population is the entire group of individuals that you are interested in studying.
- Determine the sample size. The sample size is the number of individuals that you will select from the population.
- Assign numerical values to each individual in the population. You can do this by assigning each individual a unique number, such as their Social Security number or their employee ID number.
- Generate random numbers. You can use a random number generator to generate random numbers between 1 and the size of the population.
- Select the individuals whose numerical values match the random numbers. These individuals will be your sample.
The Basics of Random Sampling in Statistics
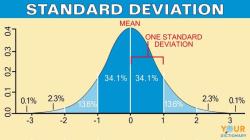
Random sampling is a statistical method that is used to select a sample from a population. Random sampling ensures that all individuals in the population have an equal chance of being selected for the sample. This is important because it helps to reduce bias in the sampling process.
There are two types of random sampling: simple random sampling and stratified random sampling.
- Simple random sampling: In simple random sampling, all individuals in the population have an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
- Stratified random sampling: In stratified random sampling, the population is divided into subgroups (strata) and then a simple random sample is selected from each stratum. This method is used to ensure that the sample is representative of the population in terms of important characteristics, such as age, gender, and race.
Methods for Conducting Random Sampling
There are a number of different methods for conducting random sampling. Some of the most common methods include:
- Lottery method: In the lottery method, each individual in the population is assigned a ticket and then a random drawing is held to select the sample.
- Random number table: A random number table is a table of random numbers that can be used to select a sample from a population.
- Computer program: There are a number of computer programs that can be used to generate random samples.
Common Errors in Random Sampling and How to Avoid Them
There are a few common errors that can be made when conducting random sampling. These errors can lead to bias in the sample and inaccurate results.
Some common errors in random sampling include:
- Self-selection bias: Self-selection bias occurs when individuals volunteer to participate in a study. This can lead to bias in the sample because individuals who volunteer to participate may be different from those who do not volunteer.
- Non-response bias: Non-response bias occurs when some individuals in the sample do not respond to the survey or interview. This can lead to bias in the sample because the individuals who respond may be different from those who do not respond.
- Convenience sampling: Convenience sampling occurs when individuals are selected for the sample because they are easy to reach. This can lead to bias in the sample because the individuals who are selected may not be representative of the population.
To avoid these errors, it is important to use a random sampling method and to follow the steps of the random sampling process carefully.
Interpreting Results from Random Sampling
When interpreting the results of a study that used random sampling, it is important to consider the following factors:
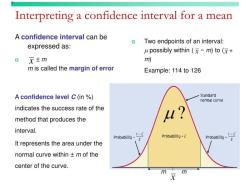
- Sample size: The larger the sample size, the more likely the results are to be representative of the population.
- Sampling method: The sampling method used can affect the accuracy of the results. For example, stratified random sampling is more likely to produce accurate results than convenience sampling.
- Response rate: The response rate is the percentage of individuals in the sample who responded to the survey or interview. A high response rate is important because it reduces the risk of non-response bias.
By considering these factors, you can better interpret the results of a study that used random sampling.
Here are some additional tips for conducting random sampling:
- Use a random number generator to generate random numbers.
- If you are using a stratified random sample, make sure that the strata are representative of the population.
- Make sure that the sample size is large enough to produce accurate results.
- Follow the steps of the random sampling process carefully.
By following these tips, you can conduct random sampling and obtain accurate results.