How many volts are in EV?
The voltage in electric vehicles (EVs) can vary depending on the specific design and configuration of the vehicle's electrical system. Generally, electric vehicles use high-voltage systems to power the electric motor and other components. The voltage in electric vehicles is typically in the range of several hundred volts to over 1,000 volts.
Here are some general points related to voltage in electric vehicles:
Battery Voltage:
- Electric vehicles are powered by high-voltage battery packs. The voltage of these battery packs can vary among different EV models and manufacturers. Common battery voltages for EVs are in the range of 200 to 800 volts.
Motor Voltage:
- The electric motor in an EV is designed to operate at a specific voltage. Motor voltage is closely tied to the voltage of the battery pack, and it is a critical factor in determining the overall performance of the vehicle.
High-Voltage Systems:
- EVs use high-voltage systems for improved efficiency in power transmission and to reduce the current flow, which helps in minimizing energy losses. High-voltage systems also allow for more compact and lightweight components.
Charging Voltage:
- When charging an electric vehicle, the charging voltage will depend on the charging infrastructure and the charging equipment used. Common levels of charging include Level 1 (120 volts AC), Level 2 (240 volts AC), and DC fast charging, which can operate at higher voltages.
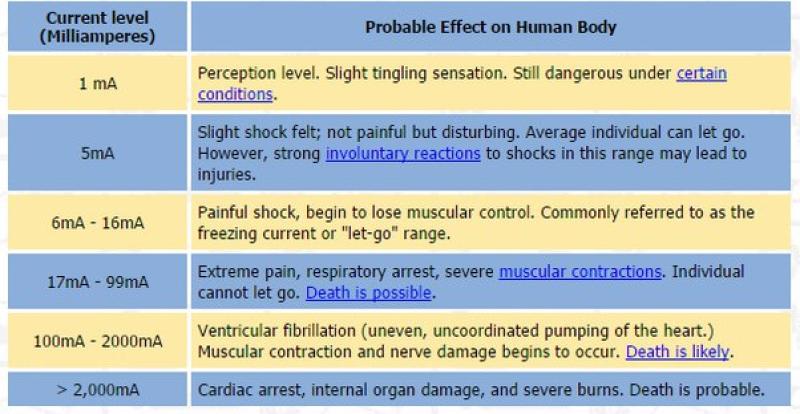
Safety Considerations:
- High-voltage systems in electric vehicles require careful engineering for safety. EVs are equipped with safety features and systems to protect occupants and first responders in the event of an accident or other emergency.
It's important to note that the voltage of electric vehicles is just one aspect of their electrical systems. Other factors, such as current, power, and energy capacity, also play crucial roles in determining the overall performance and range of an electric vehicle.
The specific voltage of a particular electric vehicle can be found in the vehicle's technical specifications provided by the manufacturer. As technology advances, electric vehicles are continually evolving, and there may be variations in voltage levels among different generations and models.
How many volts does an Electric Vehicle (EV) typically operate on?
Electric vehicles (EVs) typically operate on a voltage range of 300 to 400 volts. This voltage range is sufficient to power the electric motor and other components of the EV, while also being safe for passengers and the environment.
Here is a table of the typical voltage ranges for different types of EVs:
| EV Type | Typical Voltage Range |
|---|---|
| Passenger cars | 300-400 volts |
| Buses and trucks | 600-800 volts |
| Motorcycles | 72-144 volts |
| Scooters | 48-72 volts |
Some EVs, such as the Porsche Taycan, use an 800-volt system. This higher voltage allows for faster charging and more efficient power delivery to the motor. However, 800-volt systems are still relatively new and not as widely available as 400-volt systems.
The voltage of an EV is determined by a number of factors, including the size and power of the motor, the battery capacity, and the desired range. In general, larger and more powerful EVs require higher voltages.
Here are some of the benefits of using a higher voltage in an EV:
- Faster charging: Higher voltages allow for faster charging times. This is because higher voltages can push more current through the charging cables, which allows the battery to charge more quickly.
- More efficient power delivery: Higher voltages can also be more efficient at delivering power to the motor. This is because higher voltages reduce the amount of electrical resistance in the system, which reduces heat loss and improves overall efficiency.
- Longer range: Higher voltages can also contribute to longer range. This is because higher voltages allow the battery to store more energy, which means the EV can travel further on a single charge.
However, there are also some drawbacks to using a higher voltage in an EV:
- Increased cost: Higher voltage systems are typically more expensive than lower voltage systems. This is because they require more specialized components, such as high-voltage cables and connectors.
- Increased safety concerns: Higher voltages can be more dangerous than lower voltages. This is because higher voltages can cause more severe electrical shocks.
Overall, the voltage of an EV is a critical factor that affects the performance, efficiency, and safety of the vehicle. As EV technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even higher voltage systems become more common.