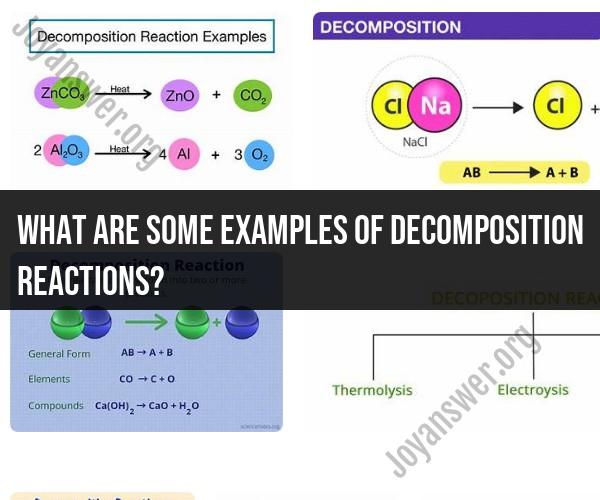
What are some examples of decomposition reactions?
Decomposition reactions are chemical reactions in which a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. These reactions are the opposite of synthesis reactions, where two or more substances combine to form a more complex one. Here are some examples of decomposition reactions:
Thermal Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate:
- Reaction: CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
- Explanation: When calcium carbonate (found in limestone and chalk) is heated, it decomposes into calcium oxide (quicklime) and carbon dioxide gas.
Electrolysis of Water:
- Reaction: 2 H2O (l) → 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g)
- Explanation: When an electric current is passed through water, it decomposes into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas.
Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide:
- Reaction: 2 H2O2 (aq) → 2 H2O (l) + O2 (g)
- Explanation: Hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water and oxygen gas, especially in the presence of a catalyst like manganese dioxide.
Decomposition of Sodium Bicarbonate (Baking Soda):
- Reaction: 2 NaHCO3 (s) → Na2CO3 (s) + H2O (g) + CO2 (g)
- Explanation: When baking soda is heated, it decomposes into sodium carbonate, water vapor, and carbon dioxide gas, which causes baked goods to rise.
Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium Nitrate:
- Reaction: NH4NO3 (s) → N2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)
- Explanation: Ammonium nitrate, a common component of fertilizers and explosives, decomposes when heated to produce nitrogen gas and water vapor.
Decomposition of Silver Chloride with Light:
- Reaction: 2 AgCl (s) → 2 Ag (s) + Cl2 (g)
- Explanation: When silver chloride is exposed to light, it decomposes into silver metal and chlorine gas.
Decomposition of Hydrogen Sulfide:
- Reaction: 2 H2S (g) → 2 H2 (g) + S2 (g)
- Explanation: Hydrogen sulfide gas decomposes into hydrogen gas and sulfur vapor.
Decomposition of Nitrogen Triiodide:
- Reaction: 2 NI3 (s) → N2 (g) + 3 I2 (g)
- Explanation: Nitrogen triiodide is an unstable compound that decomposes explosively into nitrogen gas and iodine vapor when disturbed.
Decomposition of Sodium Azide:
- Reaction: 2 NaN3 (s) → 3 N2 (g) + 2 Na (s)
- Explanation: Sodium azide decomposes, often explosively, into nitrogen gas and sodium metal.
Decomposition of Ozone:
- Reaction: 3 O3 (g) → 3 O2 (g)
- Explanation: Ozone (O3) decomposes into molecular oxygen (O2) under certain conditions, such as exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
These examples illustrate various types of decomposition reactions, from thermal decomposition to light-induced decomposition and electrolysis. Decomposition reactions are important in various chemical and industrial processes and play a crucial role in chemistry and everyday life.
Understanding Decomposition Reactions in Chemistry
A decomposition reaction is a chemical reaction in which a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler compounds or elements. Decomposition reactions can be caused by heat, light, electricity, or other catalysts.
Decomposition reactions are the opposite of combination reactions, in which two or more compounds combine to form a single compound. Decomposition reactions are also important in many natural and industrial processes.
Examples of Decomposition Reactions in Nature and Industry
Here are some examples of decomposition reactions in nature and industry:
- In nature:
- The decomposition of leaves and other organic matter in the soil by bacteria and fungi
- The decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen by sunlight during photosynthesis
- The decomposition of carbon dioxide into carbon and oxygen by volcanoes and other geological processes
- In industry:
- The decomposition of limestone into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide during cement production
- The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen in rocket fuel
- The decomposition of organic matter into methane and other gases in landfills
Key Characteristics and Mechanisms of Decomposition Reactions
Some key characteristics and mechanisms of decomposition reactions include:
- Decomposition reactions are typically endothermic, meaning that they require energy to occur.
- The rate of a decomposition reaction can be affected by temperature, pressure, and the presence of catalysts.
- Decomposition reactions can occur in a variety of ways, including:
- Thermal decomposition: Decomposition caused by heat
- Photodecomposition: Decomposition caused by light
- Electrochemical decomposition: Decomposition caused by electricity
- Catalytic decomposition: Decomposition accelerated by the presence of a catalyst
Safety Considerations for Handling Decomposition Reactions
Some decomposition reactions can be dangerous, especially if they produce toxic or flammable gases. It is important to follow safety precautions when handling decomposition reactions, such as:
- Conducting the reaction in a well-ventilated area
- Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and a respirator
- Being aware of the potential hazards of the reactants and products of the reaction
Decomposition Reactions in Environmental Processes
Decomposition reactions play an important role in many environmental processes, such as:
- The decomposition of organic matter in the soil helps to cycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- The decomposition of organic matter in landfills produces methane, a greenhouse gas that can contribute to climate change.
- The decomposition of water pollutants, such as sewage and industrial waste, helps to clean up the environment.
Overall, decomposition reactions are an important part of chemistry and nature. They are used in a variety of industrial and environmental processes, and they play a vital role in the cycling of matter in the ecosystem.