What is the formula for decomposition reactions?
Formula for Decomposition Reactions: Explanation and Example
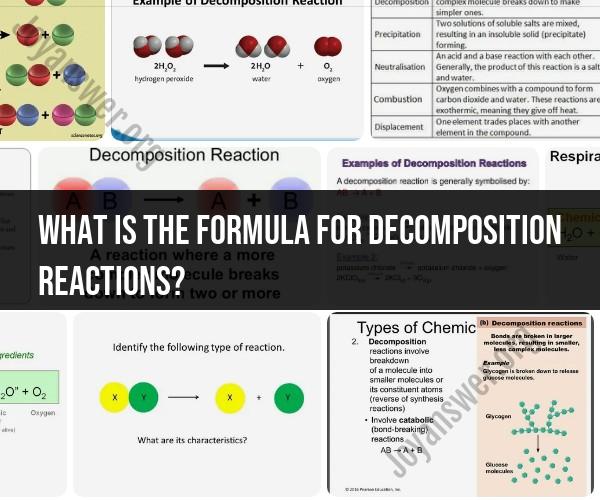
A decomposition reaction is a type of chemical reaction where a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. The general formula for a decomposition reaction is:
AB → A + B
In this formula:
- "AB" represents the initial compound that undergoes decomposition.
- "A" and "B" represent the simpler substances produced as a result of the reaction.
Decomposition reactions can be triggered by various factors, such as heat, light, electricity, or the presence of other chemicals. Let's look at an example to illustrate the formula and concept of decomposition reactions:
Example: Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide
One common example of a decomposition reaction is the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into water (H2O) and oxygen (O2). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2
In this equation:
- "2 H2O2" represents two molecules of hydrogen peroxide.
- "2 H2O" represents two molecules of water.
- "O2" represents one molecule of oxygen.
When hydrogen peroxide decomposes, it releases oxygen gas and forms water. This reaction can be catalyzed by various substances, including the enzyme catalase found in living organisms.
It's important to note that decomposition reactions can involve various types of compounds, including binary compounds (compounds consisting of two elements), metal carbonates, metal hydroxides, and more. The specific products of the reaction will depend on the composition of the initial compound and the conditions under which the reaction occurs.
Overall, decomposition reactions play a significant role in both natural processes and laboratory settings. They help break down complex molecules into simpler components, releasing energy in the process.