Can someone please explain the universal law of gravitation?
Certainly! The Universal Law of Gravitation, formulated by Sir Isaac Newton in 1687, is a fundamental principle in physics that describes the force of gravity between two objects. This law demystifies how objects are attracted to each other due to their masses. Here's an explanation of the Universal Law of Gravitation:
The Law:
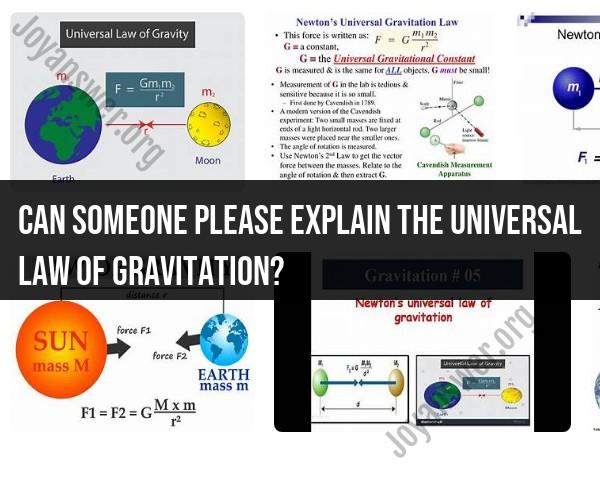
The Universal Law of Gravitation states that every point mass attracts every other point mass by a force acting along the line intersecting both points. This force is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The Formula:
The mathematical representation of this law is as follows:
Where:
- represents the gravitational force between the two objects.
- is the gravitational constant, which is a universal constant that has the same value throughout the universe.
- and are the masses of the two objects.
- is the distance between the centers of the two objects.
Key Points:
Inverse Square Law: The law shows that the force of gravity decreases as the square of the distance between two objects increases. In other words, if you double the distance between two objects, the gravitational force becomes one-fourth of what it was at the original distance.
Proportional to Mass: The force of gravity is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the two objects. This means that if you increase the mass of one or both objects, the gravitational force between them also increases.
Gravitational Constant: The constant is a fundamental constant of nature. It's a very small number, and its value was determined through experiments. It ensures that the units used in the formula are consistent and that the law applies universally.
Applicability: The Universal Law of Gravitation applies not only to objects on or near Earth but to all objects with mass in the universe. It's what keeps planets in orbit around the Sun, the Moon orbiting Earth, and satellites in orbit around Earth.
Weight: On Earth, the weight of an object is the result of the gravitational force acting on it due to the Earth's mass. Weight is equal to the mass of an object multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s² on Earth).
Action and Reaction: According to Newton's third law of motion, the force of gravity is mutual. If object A exerts a gravitational force on object B, object B simultaneously exerts an equal and opposite gravitational force on object A.
The Universal Law of Gravitation is a foundational principle of classical physics and has played a crucial role in our understanding of the universe. It explains why celestial bodies are attracted to each other and why objects fall to the ground when dropped. Additionally, this law forms the basis for understanding orbits, the motion of planets, and the behavior of objects in space.
Understanding the Universal Law of Gravitation
The Universal Law of Gravitation is a physical law that describes the attractive force between any two objects with mass. The law was discovered by Sir Isaac Newton in the late 17th century and is one of the most fundamental laws in physics.
The law states that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. In other words, the more massive an object is, and the closer it is to another object, the stronger the gravitational force between them will be.
The Universal Law of Gravitation can be expressed mathematically as follows:
F = G * (m1 * m2) / r^2
where:
- F is the force of gravity between the two objects
- G is the gravitational constant, a universal constant that has the same value for all objects
- m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects
- r is the distance between the two objects
Sir Isaac Newton and the Discovery of Gravitational Law
Sir Isaac Newton was an English physicist and mathematician who is considered one of the most influential scientists of all time. He is credited with discovering the Universal Law of Gravitation, as well as the laws of motion and optics.
Newton's discovery of the Universal Law of Gravitation was a major breakthrough in physics. It provided a unified explanation for a wide range of phenomena, including the motion of planets and comets, the tides, and the fall of objects to the ground.
Key Principles of the Universal Law of Gravitation
The Universal Law of Gravitation is based on the following key principles:
- Every object in the universe attracts every other object with mass.
- The force of gravity is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the two objects.
- The force of gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two objects.
- The gravitational force is always attractive.
Applications and Implications of Gravitational Theory
The Universal Law of Gravitation has a wide range of applications and implications. It is used to calculate the trajectories of spacecraft, design bridges and other structures, and predict the behavior of stars and galaxies.
The law also has important implications for our understanding of the universe. It suggests that the universe is a unified whole, and that all objects in the universe are interconnected.
Modern Scientific Insights into Gravitational Forces
The Universal Law of Gravitation is one of the most well-tested laws in physics. However, there are still some aspects of gravity that scientists do not fully understand.
For example, scientists are still working to develop a unified theory of gravity that can explain both the large-scale gravity of galaxies and the small-scale gravity of atoms and subatomic particles.
Scientists are also studying the possibility of the existence of dark matter and dark energy, two mysterious substances that are thought to play a role in gravity.
Despite the many unanswered questions, the Universal Law of Gravitation remains one of the most important and fundamental laws in physics. It provides a foundation for our understanding of the universe and how it works.