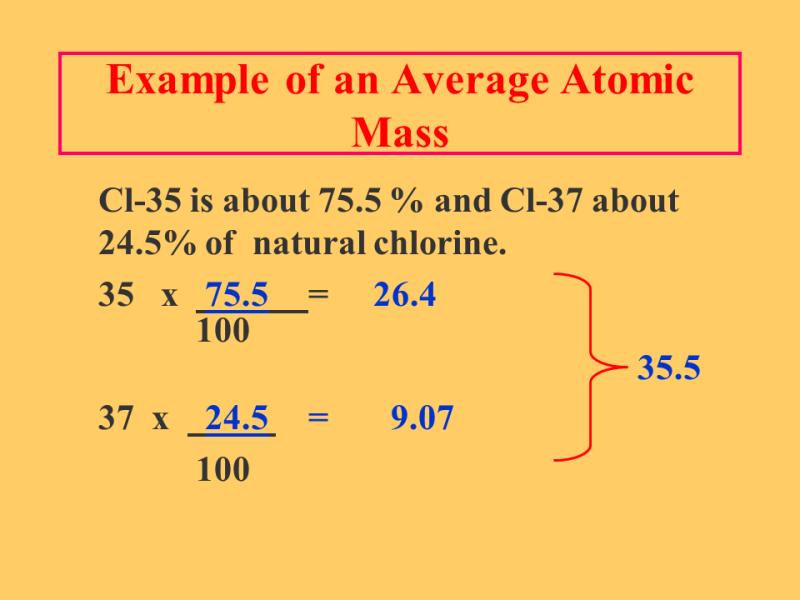
What is average atomic mass and how is it calculated?
Average atomic mass is a weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element, taking into account their abundance in a given sample. Isotopes are variants of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different atomic masses.
The formula for calculating average atomic mass () is as follows:
Here:
- represents the mass of each isotope of the element.
- represents the natural abundance (percentage) of each isotope.
The result is the weighted average atomic mass expressed in unified atomic mass units (u or amu).
Let's take carbon as an example:
- Carbon-12 () has an abundance of approximately 98.89%.
- Carbon-13 () has an abundance of approximately 1.11%.
The average atomic mass of carbon () is calculated as follows:
This average atomic mass, approximately 12.0111 u, is the value typically found on the periodic table for carbon.
The significance of average atomic mass lies in its practical use in chemistry and physics:
Chemical Calculations:
- Average atomic mass is used in chemical calculations, such as determining the amount of a substance in moles or predicting the behavior of gases.
Elemental Identification:
- The value of average atomic mass helps identify the element, as it reflects the average mass of atoms present in a naturally occurring sample.
Mass Spectrometry:
- Mass spectrometry experiments provide data on the masses and abundances of isotopes, contributing to the determination of average atomic mass.
Stoichiometry:
- In stoichiometry, the relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions, average atomic mass is used to convert between mass and moles.
Research and Analysis:
- Scientists use average atomic mass in various research fields, including environmental science, geology, and astrophysics, where isotopic compositions provide valuable information.
Understanding the concept of average atomic mass is fundamental to interpreting and predicting the behavior of elements in chemical and physical processes. It reflects the real-world distribution of isotopes and their contributions to the overall mass of an element.
What constitutes the average atomic mass of an element?
The average atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of the masses of its isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. The mass of an isotope is determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Protons have a mass of approximately 1.007 atomic mass units (u), while neutrons have a mass of approximately 1.009 u.
How is the average atomic mass calculated for isotopes?
To calculate the average atomic mass of an element, you need to know the masses of its isotopes and their relative abundances. The relative abundance of an isotope is the percentage of atoms of the element that are that isotope.
Example:
Element: Lithium (Li)
Isotopes: ⁷Li (7 protons, 4 neutrons) and ⁶Li (6 protons, 3 neutrons)
Relative abundance: 92.5% of Li atoms are ⁷Li and 7.5% of Li atoms are ⁶Li
Average atomic mass:
(92.5% * 7.017 u) + (7.5% * 6.015 u) = 6.941 u
What significance does the average atomic mass hold in chemistry?
The average atomic mass of an element is an important concept in chemistry because it is used to calculate the molar mass of compounds and to balance chemical equations. The molar mass of a compound is the mass of one mole of the compound, which is defined as 6.022 x 10^23 atoms or molecules.
The average atomic mass is also used to predict the properties of elements. For example, elements with higher average atomic masses tend to be denser and have higher melting and boiling points than elements with lower average atomic masses.