How does a binary converter work?
A binary converter is a tool or program that facilitates the conversion of numbers or data from one numerical system, typically the binary system, to another numerical system, such as decimal, hexadecimal, or octal. Here's how binary converters work:
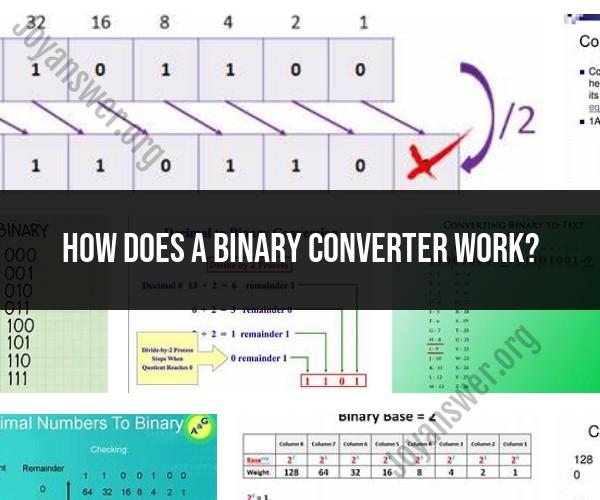
Input: Binary converters take an input value or data represented in the binary system. In the binary system, data is expressed using only two symbols: 0 and 1. For example, the binary number "1010" represents the decimal number 10.
Conversion Algorithm: Binary converters use algorithms to interpret and convert the binary input into the desired numerical system. Each numerical system has its own set of rules and symbols for representing numbers.
Decimal Conversion: To convert binary to decimal, the converter typically follows these steps:
- Starting from the right (the least significant bit), assign a positional value of 2^0 to the rightmost bit (which is 1).
- Assign a positional value of 2^1 to the next bit to the left (which is 0).
- Continue assigning increasing powers of 2 to each bit as you move from right to left.
- Multiply each bit's value (0 or 1) by its positional value and sum them all to get the decimal equivalent.
For example, to convert "1010" to decimal:
- (1 * 2^3) + (0 * 2^2) + (1 * 2^1) + (0 * 2^0) = 8 + 0 + 2 + 0 = 10
Hexadecimal and Octal Conversion: Binary converters can also convert binary to hexadecimal or octal. These conversions involve grouping binary digits into sets and then converting each set into the corresponding hexadecimal or octal digit. Hexadecimal uses base-16 and octal uses base-8, so they have their own sets of symbols (0-9 and A-F for hexadecimal, and 0-7 for octal) to represent values.
For example, "1010 1101" in binary can be grouped into "1010" and "1101." Converting these groups to hexadecimal and octal yields "A" and "15" in hexadecimal, and "12" in octal.
Output: The binary converter provides the output in the desired numerical system, which can be a decimal, hexadecimal, octal, or other base.
Reverse Conversion: Some binary converters may also support reverse conversion, allowing you to convert numbers from decimal, hexadecimal, or octal back to binary.
Binary converters are commonly used in computer science, digital electronics, and programming to work with binary data representations, as well as in educational contexts to help students understand different numerical systems and conversions between them. They simplify the process of converting between different bases, making it more accessible to individuals who may not be familiar with the underlying mathematics.