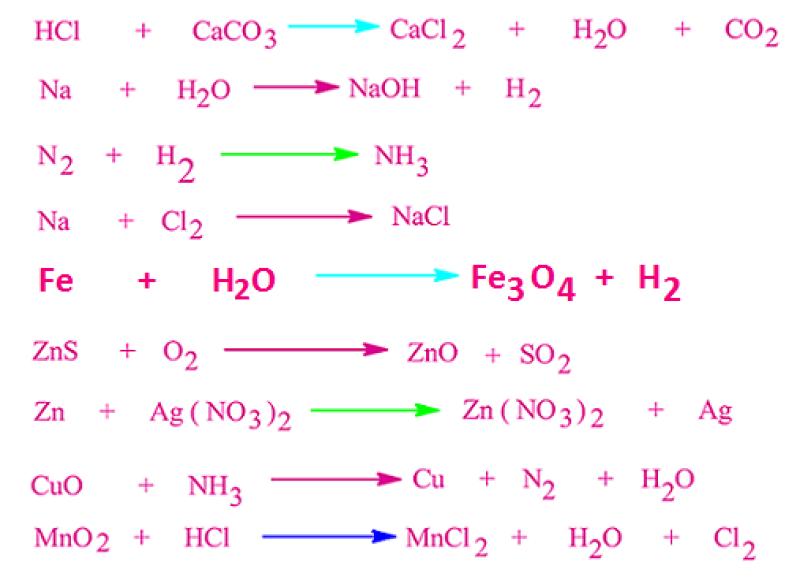
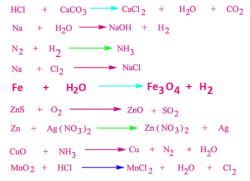
How to write unbalanced equations?
To write an unbalanced chemical equation, you can follow these steps:
Identify the Reactants and Products:
- Determine the reactants (substances that are undergoing a chemical change) and the products (substances that are formed as a result of the chemical reaction).
Write the Chemical Symbols and Formulas:
- Use chemical symbols and formulas to represent the reactants and products. If you're not given the formulas, you might need to look them up in a chemical reference or periodic table.
Write the Unbalanced Equation:
- Place the chemical formulas for the reactants on the left side of the arrow ("→") and the formulas for the products on the right side.
- Do not worry about balancing the equation at this stage; just write it as you identify the reactants and products.
Verify the Law of Conservation of Mass:
- The next step is to ensure that the unbalanced equation obeys the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that the number of atoms of each element on the left side of the equation must be equal to the number of atoms of the same element on the right side.
Balance the Equation:
- To balance the equation, adjust the coefficients (whole numbers) in front of the chemical formulas on the left and right sides of the equation. Coefficients indicate the relative number of molecules or moles involved in the reaction.
- Start by balancing the most complex or least common elements first, such as polyatomic ions or compounds with multiple atoms.
- Avoid changing the subscripts within chemical formulas, as this would alter the identity of the compounds.
- You can only balance equations by changing the coefficients, not by altering the chemical formulas themselves.
Verify Mass Conservation:
- After balancing, double-check that the equation satisfies the Law of Conservation of Mass. Ensure that the number of atoms of each element on the left side is equal to the number of atoms of the same element on the right side.
Reduce to Simplest Whole Numbers:
- If necessary, reduce coefficients to the simplest whole numbers to express the smallest whole-number ratio.
Final Equation:
- Once the equation is balanced, you have your final balanced chemical equation.
Balancing chemical equations may require trial and error, but it's important to ensure that the equation obeys the Law of Conservation of Mass, which is a fundamental principle in chemistry. It's also a valuable skill for understanding and predicting chemical reactions.
Writing Unbalanced Equations: Techniques and Applications
Unbalanced chemical equations represent chemical reactions without specifying the exact coefficients of the reactants and products. While balanced equations provide a more detailed and accurate representation of chemical reactions, unbalanced equations still serve valuable purposes in understanding and predicting chemical processes.
Techniques for Writing Unbalanced Equations
Writing unbalanced equations involves identifying the reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction and expressing them using their chemical formulas. Here are some key techniques:
Identify the reactants and products: Determine the substances that undergo the chemical change and the substances formed as a result of the reaction.
Write the chemical formulas: Represent the reactants and products using their correct chemical formulas, including subscripts to indicate the number of atoms of each element.
Separate reactants and products with an arrow: Use an arrow (→) to indicate the direction of the chemical reaction.
Use coefficients to balance atoms: Although not necessary for unbalanced equations, coefficients can be initially used to balance the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation. This can aid in identifying the correct products and ensuring the reaction is feasible.
Applications of Unbalanced Equations
Unbalanced equations serve various purposes in chemistry:
Preliminary representations: They provide a quick and concise way to represent chemical reactions before balancing.
Identifying reaction types: They can help identify the type of chemical reaction, such as synthesis, decomposition, combustion, single displacement, double displacement, or acid-base reaction.
Predicting products: Based on the reactants and the type of reaction, unbalanced equations can help predict the possible products formed.
Guiding laboratory experiments: They can serve as starting points for designing laboratory experiments to investigate chemical reactions.
The Art of Formulating Unbalanced Chemical Equations
Formulating unbalanced chemical equations requires a combination of knowledge and intuition. By understanding the basic principles of chemical reactions, the types of bonds involved, and the reactivity of different elements, one can make informed predictions about the products formed and the overall reaction process.
Unbalanced Equations and Their Role in Chemistry
Unbalanced equations play a crucial role in the study and application of chemistry. They provide a simplified representation of chemical reactions, allowing for quick identification of reactants, products, and reaction types. While not as detailed as balanced equations, unbalanced equations serve as valuable tools for understanding, predicting, and experimenting with chemical reactions.