What are the basics of Microbiology?
Microbiology encompasses the study of microorganisms, which are microscopic living organisms that exist in various forms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and some algae. Understanding the basics of microbiology involves several fundamental concepts:
Microorganisms: Microbiology focuses on the study of microorganisms, which are ubiquitous and diverse. They play essential roles in various ecosystems, including human health, industry, agriculture, and the environment.
Classification: Microorganisms are classified into different groups based on their characteristics, such as structure, metabolism, and genetic makeup. This classification helps in understanding their diversity and relationships.
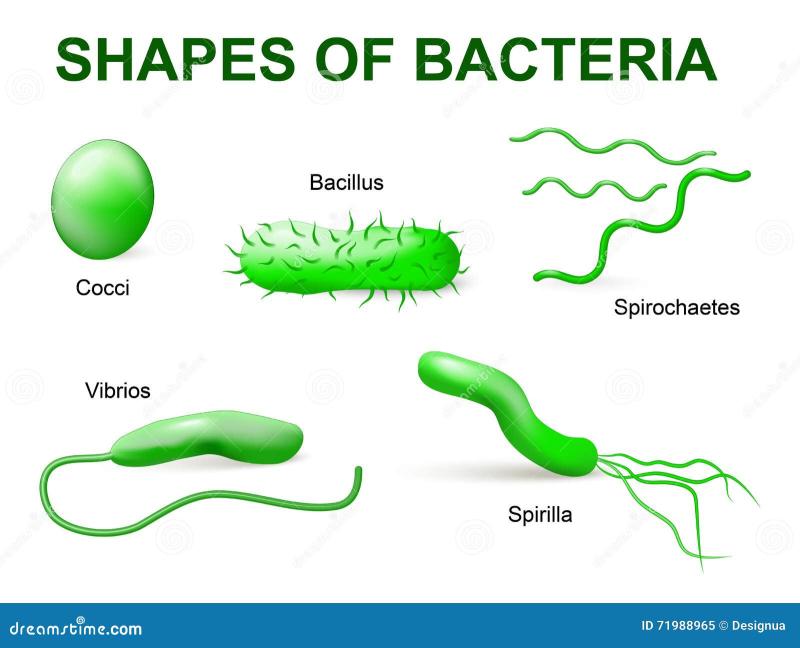
Cellular Structure: Microorganisms can be unicellular (consisting of a single cell) or multicellular. They exhibit various cellular structures, such as cell walls, membranes, organelles, and diverse shapes (e.g., spherical, rod-shaped, spiral).
Bacterial Structure: Bacteria are prokaryotic cells lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They have a cell wall, plasma membrane, genetic material (DNA), and often possess flagella or pili for movement and attachment.
Viral Structure: Viruses are non-cellular entities containing genetic material (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat. They require a host cell to replicate and cause infections in various organisms.
Fungal Structure: Fungi can be unicellular (yeasts) or multicellular (molds). They have eukaryotic cells with a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and cell walls made of chitin. Fungi play roles in decomposition, medicine, and food production.
Protozoa: Protozoa are single-celled eukaryotic organisms found in diverse habitats. They move by pseudopods, cilia, or flagella. Some protozoa are pathogens, while others are essential components of ecosystems.
Microbial Growth and Reproduction: Microorganisms reproduce through various methods like binary fission, budding, spore formation, or viral replication. Factors influencing growth include temperature, pH, nutrients, and environmental conditions.
Role in Health and Disease: Microbiology explores the interaction between microorganisms and their hosts. Some microorganisms are beneficial (probiotics), while others cause infectious diseases (pathogens).
Applications: Microbiology has applications in various fields, including medicine (antibiotics, vaccines), biotechnology (genetic engineering, fermentation), environmental science, agriculture, and food industry (food preservation, fermentation).
Understanding these fundamental concepts provides a foundation for studying the diverse world of microorganisms and their impact on life, health, and the environment.
What are the foundational concepts and principles taught in a basic Microbiology course?
A basic Microbiology course lays the foundation for understanding the fascinating world of microscopic life. Here are some key concepts and principles you can expect to encounter:
1. The Diversity of Microorganisms:
- Different Types of Microbes: Learn about the classification of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses. Discover their unique characteristics, habitats, and roles in the biosphere.
- Microbial Structure and Function: Explore the basic structure of different microbes, from the simple cell wall of bacteria to the complex eukaryotic cells of fungi. Understand how their structure relates to their function and survival.
- Microbial Metabolism: Delve into how microbes obtain energy and nutrients. Investigate diverse metabolic pathways like photosynthesis, respiration, and fermentation, recognizing their significance for both microbes and the environment.
2. Growth and Reproduction of Microorganisms:
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction: Understand the different ways microbes reproduce, including binary fission, budding, and spore formation. Explore the concept of conjugation and its role in genetic exchange.
- Factors Affecting Microbial Growth: Discover the environmental factors like temperature, pH, oxygen availability, and nutrient availability that influence microbial growth and reproduction. Appreciate the concept of optimal and limiting factors.
- Microbial Control Methods: Learn about various methods used to control microbial growth, including physical methods like heat or filtration, chemical methods like disinfectants, and biological methods like antibiotics.
3. The Role of Microbes in the Environment and Human Health:
- Environmental Microbiology: Understand the vital roles microbes play in the environment, including nutrient cycling, decomposition, and bioremediation. Explore their involvement in maintaining ecological balance.
- Medical Microbiology: Discover the diverse ways microbes can interact with humans, ranging from beneficial symbiosis to pathogenic infections. Learn about common pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and parasites, and how they cause disease.
- Applied Microbiology: Investigate the various applications of microbes in industry, agriculture, and medicine. Explore examples like production of antibiotics and vaccines, fermentation processes in food production, and bioremediation technologies.
4. Laboratory Techniques in Microbiology:
- Basic Laboratory Skills: Develop practical skills in aseptic technique, culture media preparation, microscopy, and staining techniques. Learn how to safely handle and study microbial cultures.
- Experimental Design and Data Analysis: Gain an understanding of basic scientific principles like the scientific method, hypothesis testing, and data analysis. Apply these principles to design and interpret simple microbiology experiments.
Beyond these foundational concepts, a basic Microbiology course may also introduce you to:
- Antimicrobial resistance and its global implications.
- Emerging infectious diseases and public health concerns.
- The microbiome and its role in human health.
- Ethical considerations in microbiology research and applications.
Remember, this is just a snapshot of the exciting world explored in a basic Microbiology course. By delving deeper into these concepts and principles, you'll gain a crucial understanding of the microscopic life that surrounds us and its profound impact on our planet and well-being.