What is an example of a combustion reaction?
A combustion reaction, also known as a combustion process, is a type of chemical reaction in which a substance reacts rapidly with oxygen, usually from the air, to produce heat, light, and often other products. Combustion reactions are typically exothermic, meaning they release energy in the form of heat.
The general chemical equation for a combustion reaction is:
Fuel + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
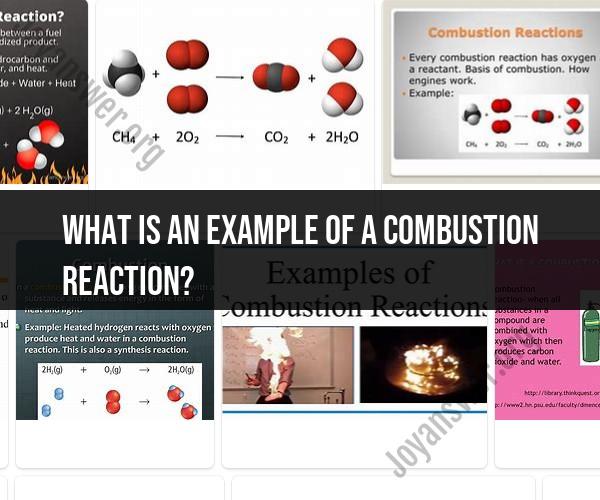
Here's an example of a combustion reaction involving the combustion of methane (CH4), which is a common component of natural gas:
Example: Combustion of Methane (CH4):
Chemical Equation:CH4 (methane) + 2O2 (oxygen) → CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 2H2O (water) + Energy
In this reaction, methane (CH4) reacts with oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and release energy in the form of heat and light.
Balanced Chemical Equation:CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Key Points:
- Combustion reactions are highly exothermic and release a significant amount of energy in the form of heat and light.
- Oxygen is a key reactant in combustion reactions. It is often readily available in the atmosphere, making combustion reactions common in the natural world.
- Combustion reactions are essential for various processes, including energy production (burning of fuels), cooking, and providing heat.
- Incomplete combustion, which occurs when there is limited oxygen, can lead to the formation of byproducts such as carbon monoxide (CO) and soot.
It's important to note that not all reactions involving oxygen are combustion reactions. Combustion reactions are characterized by their rapid and highly exothermic nature, resulting in the production of heat and light.