What are the different types of chemical reactions?
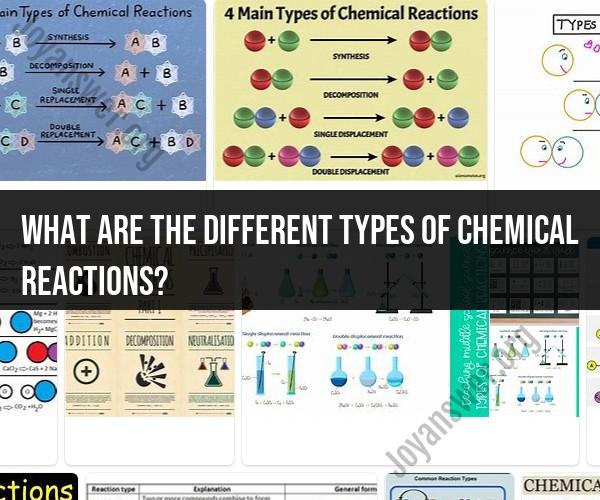
Chemical reactions can be categorized into several different types based on the changes that occur in the chemical composition and structure of the substances involved. Here's a brief overview of the main types of chemical reactions:
Combination Reactions (Synthesis):
- In a combination reaction, two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
- The general form is: A + B → AB
- Example: The combination of hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) to form water (H2O): 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O.
Decomposition Reactions:
- In a decomposition reaction, a single reactant breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
- The general form is: AB → A + B
- Example: The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into water (H2O) and oxygen (O2): 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2.
Single Replacement Reactions (Displacement):
- In a single replacement reaction, one element replaces another element in a compound.
- The general form is: A + BC → AC + B
- Example: The reaction between zinc (Zn) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) to produce zinc chloride (ZnCl2) and hydrogen (H2): Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2.
Double Replacement Reactions (Metathesis):
- In a double replacement reaction, ions from two different compounds exchange places to form new compounds.
- The general form is: AB + CD → AD + CB
- Example: The reaction between silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium chloride (NaCl) to produce silver chloride (AgCl) and sodium nitrate (NaNO3): AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3.
Combustion Reactions:
- Combustion reactions involve the rapid reaction of a substance with oxygen, often producing heat and light.
- Commonly seen in the burning of fuels such as hydrocarbons.
- Example: The combustion of methane (CH4) in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O): CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O.
Redox Reactions (Oxidation-Reduction):
- Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between reactants.
- One substance is oxidized (loses electrons), and another is reduced (gains electrons).
- Example: The reaction between iron (Fe) and oxygen (O2) to form iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3), where iron is oxidized from Fe to Fe3+ and oxygen is reduced from O2 to O2-: 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3.
Acid-Base Reactions (Neutralization):
- Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of protons (H+ ions) between an acid and a base to produce water and a salt.
- Example: The reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form water (H2O) and sodium chloride (NaCl): HCl + NaOH → H2O + NaCl.
These are fundamental types of chemical reactions, and many real-world chemical processes can be understood by recognizing these reaction types. Understanding the types of reactions is essential in chemistry, as it helps predict the products of reactions and analyze chemical changes.