How to find the neutral axis length of a sheet metal?
The neutral axis length of a sheet of metal is a crucial parameter in various engineering and manufacturing applications, particularly in the context of bending and forming processes. To determine the neutral axis length of a sheet metal, you can follow these general steps:
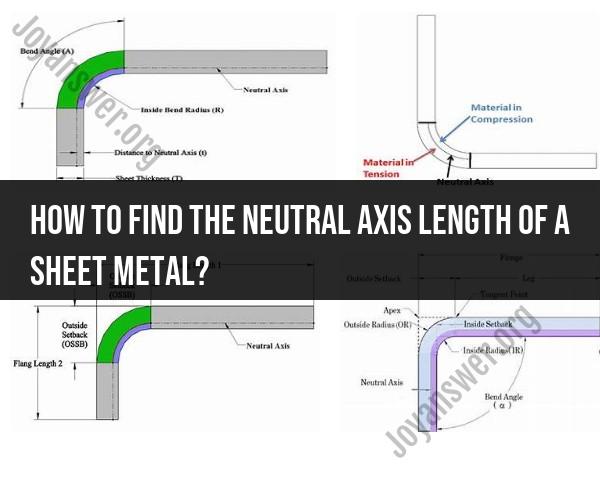
Understand the Concept: The neutral axis is an imaginary line within the cross-section of the sheet metal that does not experience any deformation during bending. It separates the material under tension (outer fibers) from the material under compression (inner fibers).
Measure the Sheet Thickness: First, measure the thickness of the sheet metal using a micrometer or a caliper. This measurement is typically denoted as "t."
Calculate the Bend Radius: If you are dealing with a bent piece of sheet metal, measure or calculate the bend radius. The bend radius is the distance from the centerline of the sheet metal to the inside surface of the bend.
Calculate the Neutral Axis: The location of the neutral axis is calculated as a function of the thickness and the bend radius. The neutral axis distance (c) from the centerline to the neutral axis can be calculated using the following formula:
c = (t * R) / (2 * R - t)
Where:
- "c" is the distance from the centerline to the neutral axis.
- "t" is the thickness of the sheet metal.
- "R" is the bend radius.
Determine the Neutral Axis Location: Once you have calculated the neutral axis distance (c), you can determine its location on the sheet metal's cross-section. It's usually measured from the inner surface (the side under compression) of the sheet metal to the neutral axis.
Please note that this calculation assumes that the sheet metal undergoes simple bending without any other complex deformation modes, such as stretching or wrinkling. In more complex bending scenarios, you may need to consider additional factors.
Keep in mind that the calculation mentioned above is a simplified method. In practice, more accurate results may require considering the specific material properties, such as the material's modulus of elasticity, and the bending process's details. For precise engineering applications, consulting with a mechanical engineer or using specialized software may be necessary to determine the neutral axis length accurately.
How to determine the neutral axis length of a sheet metal in engineering?
The neutral axis of a sheet metal is the line along which there is no strain during bending. It is located at approximately half the thickness of the sheet metal, but this can vary depending on the material and bending process.
To determine the neutral axis length of a sheet metal in engineering, you can use the following formula:
Neutral axis length = 0.5 * Sheet metal thickness * K-factor
where K-factor is a material-dependent constant that is typically between 0.3 and 0.5.
For example, to determine the neutral axis length of a 1 mm thick piece of mild steel with a K-factor of 0.4, you would use the following equation:
Neutral axis length = 0.5 * 1 mm * 0.4 = 0.2 mm
Calculating the neutral axis for different types of sheet metal configurations.
The neutral axis length can vary depending on the type of sheet metal configuration. For example, the neutral axis of a bent sheet metal part will be different from the neutral axis of a flat sheet metal part.
To calculate the neutral axis for different types of sheet metal configurations, you can use finite element analysis (FEA) software. FEA software can simulate the bending process and calculate the neutral axis length for a variety of sheet metal configurations.
The role of the neutral axis in sheet metal bending and forming processes.
The neutral axis plays an important role in sheet metal bending and forming processes. It is used to calculate the bend allowance, which is the amount of material that needs to be added to the flat sheet metal part to compensate for the material that is stretched during bending.
The neutral axis is also used to calculate the springback, which is the amount of elastic recovery that occurs after bending. Springback can be a significant factor in sheet metal bending, so it is important to calculate it accurately.
Formulas and techniques for precise neutral axis measurement.
There are a number of formulas and techniques that can be used to measure the neutral axis of a sheet metal part with precision. One common method is to use a strain gauge. Strain gauges are attached to the surface of the sheet metal part and measure the strain during bending. The neutral axis can then be calculated by plotting the strain distribution and finding the point where the strain is zero.
Another method for measuring the neutral axis is to use optical methods, such as laser scanning or digital image correlation. These methods can measure the deformation of the sheet metal part during bending and calculate the neutral axis from the deformation data.
Implications of the neutral axis length on sheet metal fabrication.
The neutral axis length has a number of implications on sheet metal fabrication. For example, the neutral axis length can affect the following:
- Bend allowance: The bend allowance is the amount of material that needs to be added to the flat sheet metal part to compensate for the material that is stretched during bending. The neutral axis length is used to calculate the bend allowance.
- Springback: Springback is the amount of elastic recovery that occurs after bending. The neutral axis length is used to calculate the springback.
- Accuracy of formed parts: The accuracy of formed parts depends on the ability to control the bending process. The neutral axis length plays an important role in controlling the bending process.
Overall, the neutral axis length is an important parameter in sheet metal fabrication. It is used to calculate the bend allowance, springback, and accuracy of formed parts.