What is the horsepower rating of an electric motor?
The horsepower (HP) rating of an electric motor is a measure of its power output. It indicates the amount of work the motor can perform over time. The formula for calculating horsepower is:
Where:
- is the power output in horsepower (HP),
- is the torque produced by the motor in pound-feet (lb-ft),
- is the rotational speed of the motor in revolutions per minute.
This formula represents the mechanical power output of the motor and is commonly used to rate the power of electric motors. The constant 5,252 is derived from the relationship between horsepower, torque, and RPM.
Alternatively, for motors with known electrical power input and efficiency, the electrical horsepower () can be calculated using the following formula:
Where:
- is the voltage of the motor in volts,
- is the current drawn by the motor in amperes,
- is the efficiency of the motor, expressed as a decimal.
It's important to note that the electrical horsepower represents the electrical power input to the motor, and the mechanical horsepower output may be less due to factors such as mechanical losses and inefficiencies.
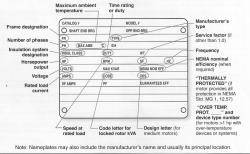
When referring to the horsepower rating of an electric motor, it typically indicates the mechanical horsepower output. The rating is often specified on the motor nameplate, providing users with information about the motor's power capacity. Motors come in various horsepower ratings, ranging from fractional horsepower (e.g., 1/4 HP) for small applications to several hundred horsepower for industrial and heavy-duty applications.
Understanding the Concept of Horsepower and its Measurement
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of power commonly used to measure the output of engines and motors. It represents the rate at which work is done, defined as the amount of energy transferred per unit of time. One horsepower is equivalent to 550 foot-pounds per second (ft-lbs/sec) or 746 watts (W).
In the context of electric motors, horsepower refers to the mechanical power output of the motor. It indicates the amount of work the motor can perform, such as rotating a shaft, driving a pump, or powering a machine. The horsepower rating of an electric motor is determined by its design characteristics, including its size, voltage, current, and efficiency.
Determining Horsepower Ratings for Different Types of Electric Motors
Electric motors come in a wide range of horsepower ratings, catering to diverse applications and power requirements. Typical horsepower ranges for different types of electric motors include:
Fractional horsepower motors: These motors typically range from 1/12 hp to 2 hp and are suitable for applications requiring low to moderate power, such as fans, blowers, and small appliances.
Integral horsepower motors: These motors range from 1 hp to 500 hp or more and are used in applications demanding higher power output, such as industrial machinery, pumps, and compressors.
High-performance motors: These motors are designed for specialized applications that require exceptional power density, efficiency, or reliability. They can reach horsepower ratings of thousands or even tens of thousands.
Calculating Horsepower Requirements for Specific Applications
Determining the appropriate horsepower rating for an electric motor is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in a specific application. Several factors influence horsepower requirements, including:
Load torque: The torque required to perform the desired task, such as lifting a weight, driving a load, or overcoming resistance.
Speed: The desired rotational speed of the motor, which determines the power output required to achieve the specified speed.
Efficiency: The efficiency of the motor, which affects the amount of power consumed to produce the desired output.
Engineers and technicians typically use calculations or reference tables to determine the horsepower requirements for specific applications. These calculations consider the load torque, speed, and efficiency factors to ensure the selected motor has sufficient power to meet the application's demands.