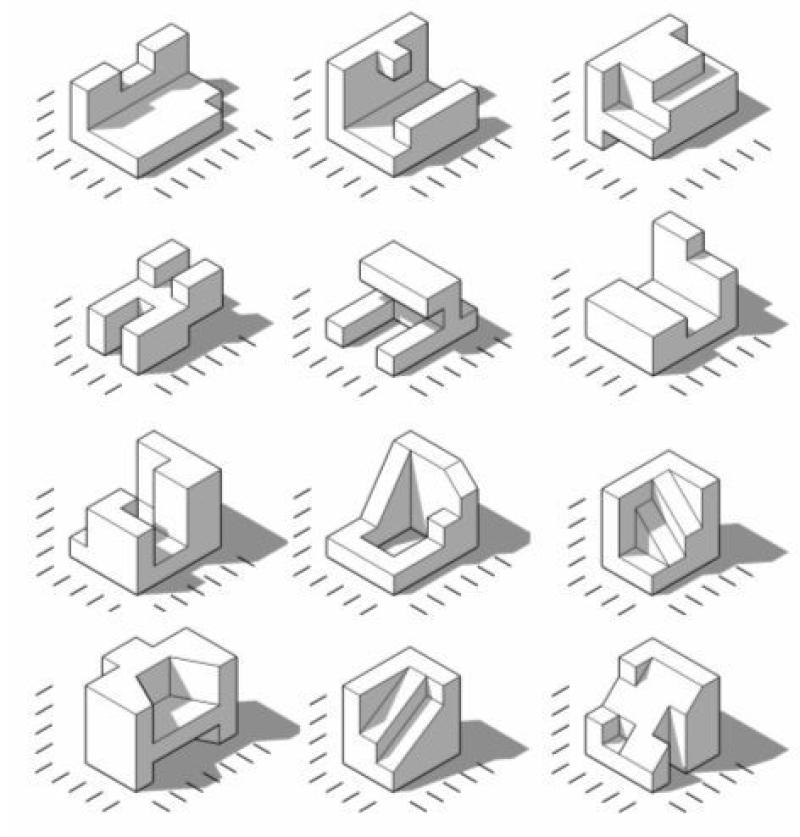
What are some uses of isometric drawings?
Isometric drawings are widely used in various technical and design applications due to their ability to represent three-dimensional objects with a more realistic sense of depth. Here are some common uses of isometric drawings:
Engineering and Technical Drawings:
- Isometric drawings are extensively used in engineering and technical fields to represent complex structures, machinery, and components. Engineers often create isometric drawings to illustrate the spatial relationships and configurations of parts in a clear and concise manner.
Architectural Design:
- Architects use isometric drawings to represent buildings and structures. These drawings help convey the layout, design, and spatial arrangement of architectural elements such as rooms, walls, and fixtures.
Piping and Plumbing Systems:
- Isometric drawings are essential in illustrating the layout of piping and plumbing systems. They provide a detailed representation of how pipes, fittings, and valves are interconnected in three-dimensional space.
Industrial Design:
- Industrial designers use isometric drawings to communicate the design of products and machinery. These drawings help convey the form, function, and assembly of industrial equipment.
Product Design and Prototyping:
- Isometric drawings are commonly used in product design to depict three-dimensional models of products. Designers use these drawings to communicate design concepts, create assembly instructions, and assist in the prototyping process.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD):
- Isometric drawings play a crucial role in computer-aided design (CAD) software. Engineers and designers use CAD tools to create precise and detailed isometric representations of objects, systems, and structures.
Educational Illustrations:
- Isometric drawings are frequently used in educational materials to teach concepts related to geometry, spatial relationships, and technical subjects. They provide a visual representation that aids in understanding complex structures.
Video Games and Animation:
- Isometric projections are often used in video game design and animation to create a visually appealing three-dimensional effect. Isometric graphics are popular for strategy games and simulations.
Technical Documentation:
- Isometric drawings are included in technical manuals and documentation to provide visual guidance on assembly, maintenance, and repair procedures. They assist technicians and operators in understanding complex systems.
Urban Planning:
- Urban planners use isometric drawings to illustrate city layouts, street plans, and the arrangement of buildings. These drawings help visualize the overall design and spatial relationships within an urban environment.
Cartography:
- Isometric projections are occasionally used in cartography to create three-dimensional maps, providing a unique perspective of landscapes and cityscapes.
Interior Design:
- Interior designers use isometric drawings to represent the layout and arrangement of furniture, fixtures, and spatial elements within a room or building.
Overall, isometric drawings are versatile tools that find applications in a wide range of industries, facilitating effective communication of spatial information and design concepts.
Sure, here is a breakdown of communicating technical information effectively, enhancing visual understanding, and applications in diverse fields using isometric drawings:
Communicating technical information effectively: Utilizing isometric drawings to illustrate three-dimensional objects
Isometric drawings play a crucial role in effectively communicating technical information, particularly when dealing with three-dimensional objects. Their ability to represent objects in a clear, concise, and distortion-free manner makes them an invaluable tool for engineers, architects, designers, and educators.
Key Advantages of Isometric Drawings for Technical Communication:
Visual Clarity: Isometric drawings provide a clear and intuitive representation of three-dimensional objects, making them easier to understand than traditional orthographic projections.
Dimensional Accuracy: Unlike perspective drawings, isometric drawings preserve object dimensions, allowing for accurate measurements and calculations.
Simplicity and Standardization: The standardized conventions and techniques used in isometric drawings ensure consistency and ease of interpretation.
Enhancing visual understanding: Employing isometric drawings to convey spatial relationships and dimensions
Isometric drawings excel at conveying spatial relationships and dimensions, making them indispensable for enhancing visual understanding.
Spatial Relationships: Isometric drawings effectively illustrate the relative positions and orientations of objects in space, aiding in understanding complex assemblies and layouts.
Dimension Visualization: The consistent scale and angle preservation in isometric drawings allow for easy visualization of object dimensions, facilitating size comparisons and spatial reasoning.
Three-Dimensional Perception: Isometric drawings provide a more intuitive representation of three-dimensional objects compared to two-dimensional drawings, enhancing spatial perception and problem-solving abilities.
Applications in diverse fields: Exploring the use of isometric drawings in architecture, engineering, design, and education
Isometric drawings find widespread applications in a variety of fields, each leveraging their unique capabilities for effective communication and understanding.
Architecture: Architects utilize isometric drawings to communicate building layouts, interior designs, and spatial arrangements, providing clear visualizations for clients and collaborators.
Engineering: Engineers employ isometric drawings to represent piping systems, mechanical components, and electrical schematics, facilitating design, analysis, and construction.
Design: Product designers use isometric drawings to showcase product designs, illustrate assembly instructions, and communicate design concepts to stakeholders.
Education: Educators incorporate isometric drawings into STEM curricula to teach spatial reasoning, geometry concepts, and technical drawing skills.
In conclusion, isometric drawings serve as a powerful tool for communicating technical information effectively, enhancing visual understanding, and supporting diverse applications across various fields. Their ability to clearly represent three-dimensional objects, preserve dimensions, and convey spatial relationships makes them an invaluable asset for engineers, architects, designers, educators, and anyone dealing with three-dimensional objects.