How do you calculate the RPM of an electric motor?
The revolutions per minute (RPM) of an electric motor can be calculated using the following formula:
Where:
- is the revolutions per minute,
- is the frequency of the power supply in hertz (Hz),
- is the number of magnetic poles in the motor.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to calculate the RPM of an electric motor:
1. Determine the Frequency:
- Find out the frequency of the power supply to the motor. In most regions, the standard power supply frequency is 60 Hz (in the United States) or 50 Hz (in many other parts of the world).
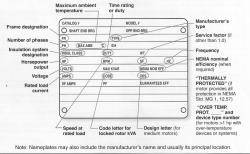
2. Identify the Number of Poles:
- The number of poles in an electric motor is a physical attribute of the motor and can be found in its specifications. It is usually even and can typically be located on the motor nameplate.
3. Plug in the Values:
- Substitute the values into the formula:
4. Calculate:
- Perform the calculations to find the RPM of the electric motor.
Example:
- Let's say you have a motor connected to a power supply with a frequency of 60 Hz, and the motor has four poles.
So, in this example, the electric motor would be operating at 900 RPM.
Additional Note:
- Some motors may have a nameplate that directly provides the rated RPM rather than the number of poles. In such cases, you can still use the formula by rearranging it:
- You can then use this formula to find the number of poles if it's not explicitly provided.
Keep in mind that this formula assumes a synchronous motor, and factors like slip (for asynchronous motors) may affect the actual operating speed. For accurate calculations related to a specific motor, it's always best to refer to the motor's technical specifications and documentation.
Understanding the Relationship between RPM and Electrical Frequency
RPM, or revolutions per minute, is a measure of rotational speed, indicating the number of complete rotations an object makes around its axis in one minute. Electrical frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), represents the number of cycles completed per second by an alternating current (AC). The relationship between RPM and electrical frequency is crucial in understanding the operation of AC motors and other electrical devices.
In AC motors, the electrical frequency supplied to the motor determines the speed at which the rotor, the rotating part of the motor, spins. This relationship is governed by the following formula:
RPM = (120 * Frequency) / Number of Poles
where:
- RPM is the rotational speed in revolutions per minute
- Frequency is the electrical frequency in Hertz (Hz)
- Number of Poles is the number of magnetic poles in the motor
For instance, a two-pole AC motor operating at a frequency of 50 Hz would have a synchronous speed of 1500 RPM (120 * 50 / 2 = 1500). Synchronous speed refers to the ideal speed at which the rotor would rotate if there were no load or resistance.
Applying the RPM Formula for Electric Motors
The RPM formula is essential for selecting and operating AC motors appropriately. By knowing the desired RPM and the available electrical frequency, engineers and technicians can determine the number of poles required for the motor. Additionally, the formula can be used to calculate the actual RPM of a motor based on its measured frequency and pole count.
Measuring and Interpreting RPM Values for Electric Motors
RPM can be measured using various methods, including tachometers, which directly measure the rotational speed of an object. In AC motors, RPM can also be indirectly determined by measuring the frequency of the motor's output voltage or current.
Interpreting RPM values for electric motors involves considering factors such as load conditions, efficiency, and torque requirements. Under no-load conditions, the actual RPM will closely match the synchronous speed calculated using the formula. As the load on the motor increases, the actual RPM will decrease due to resistance and torque requirements.
Understanding the relationship between RPM and electrical frequency is fundamental for designing, selecting, and operating AC motors effectively. By applying the RPM formula and interpreting RPM measurements, engineers and technicians can ensure that motors are operating within their intended parameters and delivering the desired performance.