What equation is used to calculate electric power?
The formula used to calculate electric power is:
Where:
- is the power in watts (W),
- is the voltage in volts (V),
- is the current in amperes (A).
This formula is known as the power equation, and it expresses the relationship between power, voltage, and current in an electrical circuit. It is based on Ohm's Law, which states that the current () flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage () across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance () between them. The power () can be calculated using the equation or, alternatively, or , where is the resistance.
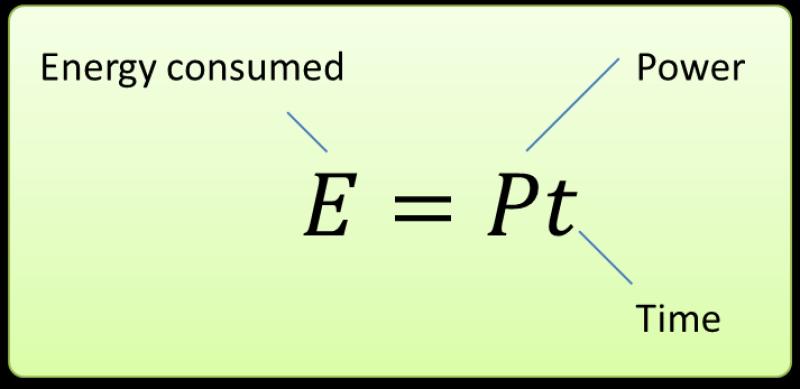
In practical terms, the power equation is crucial for understanding and managing electrical systems, as it helps calculate the amount of electrical energy consumed or produced in a circuit. Knowing the voltage and current allows for the determination of the power, which is measured in watts. It is essential for designing and analyzing electrical systems, as well as for estimating energy costs and ensuring the safe operation of devices and appliances.
Understanding the Concept of Electric Power and its Units
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit or an electric machine. It is measured in watts (W), which is the equivalent of one joule of work per second. Power can also be expressed in kilowatts (kW) or megawatts (MW), which are multiples of 1,000 and 1,000,000 watts, respectively.
Electric power is a crucial concept in understanding and managing electrical systems. It determines the amount of energy that an electrical device or appliance consumes, and it helps to ensure that electrical circuits are properly designed and sized to handle the required power load.
Introducing the Electric Power Formula
The electric power formula is P = VI, where:
- P is the electric power in watts (W)
- V is the voltage in volts (V)
- I is the electric current in amperes (A)
This formula states that electric power is directly proportional to both voltage and current. In other words, if you double the voltage or double the current, you will double the power. If you halve the voltage or halve the current, you will halve the power.
Applying the Electric Power Formula to Calculate Power Consumption
The electric power formula can be used to calculate the power consumption of any electrical device or appliance. For example, if a light bulb has a voltage of 120 V and a current of 0.5 A, then its power consumption is:
P = VI = (120 V) x (0.5 A) = 60 W
This means that the light bulb consumes 60 watts of power when it is turned on.
The electric power formula can also be used to calculate the power consumption of an entire circuit. For example, if a circuit has a voltage of 240 V and a total current of 10 A, then the power consumption of the circuit is:
P = VI = (240 V) x (10 A) = 2400 W
This means that the circuit consumes 2400 watts of power.