What quantity is Hertz used to measure?
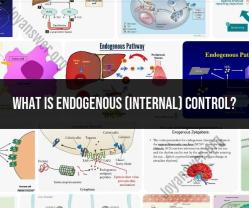
Hertz (Hz) is a unit of measurement used to quantify the frequency of a repeating event or oscillation. Specifically, Hertz measures the number of cycles or oscillations that occur in one second. In other words, it represents the frequency of a periodic phenomenon over a one-second time interval.
For example, when measuring sound, one Hertz (1 Hz) represents one cycle of a sound wave occurring in one second. Similarly, in the context of electromagnetic waves, 1 Hz corresponds to one complete oscillation of the wave in one second.
In computing and technology, Hertz is commonly used to measure the frequency or clock speed of hardware components, as mentioned in the previous response. It indicates how many cycles or operations a component can perform in one second. For instance, a CPU with a clock speed of 2 gigahertz (2 GHz) can perform 2 billion cycles or operations in one second.
In summary, Hertz is a unit of measurement for frequency, indicating the number of cycles, oscillations, or events that occur in one second, and it is used in various fields, including physics, engineering, and technology, to quantify periodic phenomena and the speed of various processes.
Understanding Hertz as a Unit of Measurement
Hertz (Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. It is named after Heinrich Hertz, a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of electromagnetic waves.
Hertz is a unit of measurement used to describe the rate of repetition of a periodic phenomenon. It can be used to measure the frequency of any type of wave, such as light waves, sound waves, and radio waves. It can also be used to measure the frequency of other types of periodic phenomena, such as the heartbeat or the flashing of a light bulb.
The Meaning of Hertz: What Does It Measure?
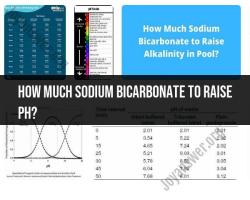
Hertz measures the number of times a periodic event occurs in one second. For example, a sound wave with a frequency of 440 Hz oscillates 440 times per second. A light wave with a frequency of 500 Hz oscillates 500 times per second.
Hertz can also be used to measure the rate at which data is transferred. For example, a network connection with a bandwidth of 100 Mbps can transfer 100 megabits of data per second.
Hertz Explained: The Physical Quantity It Represents
Hertz is a unit of measurement for frequency, which is a physical quantity that describes the rate of repetition of a periodic phenomenon. Frequency is measured in cycles per second, or hertz.
Frequency is an important concept in many areas of physics and engineering. For example, the frequency of light determines its color, and the frequency of sound determines its pitch. Frequency is also used in electronics to generate and control signals.
Here are some examples of how hertz is used to measure frequency:
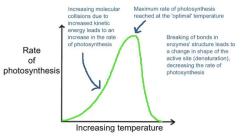
- The frequency of the electrical current in a household outlet is 60 Hz.
- The frequency of the sound of middle C on a piano is 261.6 Hz.
- The frequency of the visible light spectrum is between 400 Hz and 700 Hz.
- The frequency of a radio wave is between 300 kHz and 3 GHz.
Hertz is a versatile unit of measurement that is used in a wide variety of applications.