What is the formula to calculate acceleration?
The formula to calculate acceleration is as follows:
Acceleration (a) = Change in Velocity (Δv) / Time (Δt)
Where:
- Acceleration (a) is measured in meters per second squared (m/s²) in the International System of Units (SI).
- Change in Velocity (Δv) is the difference between the final velocity (vf) and the initial velocity (vi). It is usually measured in meters per second (m/s).
- Time (Δt) is the time interval over which the change in velocity occurs and is typically measured in seconds (s).
In summary, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity over time. If an object's velocity is increasing, it experiences positive acceleration, and if the velocity is decreasing, it experiences negative acceleration (also known as deceleration). If the velocity remains constant, the acceleration is zero.
1. Mathematical Formula for Acceleration
The mathematical formula for acceleration is:
a = Δv / Δt
where:
- a represents acceleration
- Δv represents the change in velocity (vfinal - vinitial)
- Δt represents the change in time
Acceleration is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s²), and the direction of acceleration indicates the direction in which the velocity is changing.
2. Definition of Acceleration in Physics and Motion
In physics, acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. It is a vector quantity that describes the change in both the magnitude and direction of an object's motion. Acceleration can be positive or negative, indicating whether the object's velocity is increasing or decreasing, respectively.
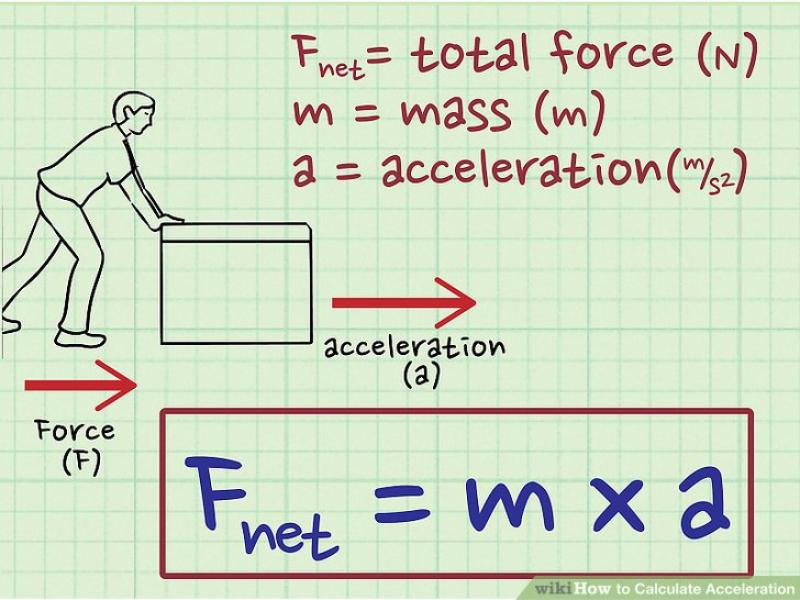
Acceleration is a fundamental concept in physics, as it is the cause of all changes in motion. According to Newton's second law of motion, the force acting on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. This law is often expressed as:
F = ma
where:
- F represents the net force acting on the object
- m represents the mass of the object
- a represents the acceleration of the object
3. Units of Measurement for Acceleration in SI
The International System of Units (SI) defines the meter per second squared (m/s²) as the standard unit of measurement for acceleration. Other commonly used units of acceleration include:
- Kilometers per hour per second (km/h/s)
- Feet per second squared (ft/s²)
- Inches per second squared (in/s²)