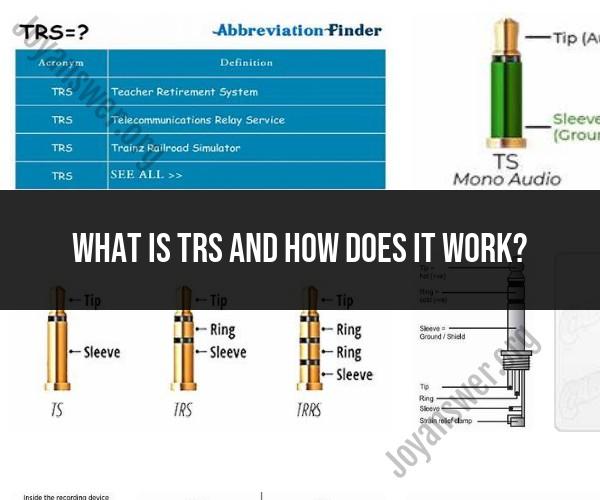
What is TRS and how does it work?
Telecommunications Relay Service (TRS) is a vital communication service that enables individuals who are deaf, hard of hearing, deaf-blind, or have speech disabilities to communicate over the telephone or other telecommunications devices. TRS helps bridge the communication gap between individuals with hearing or speech disabilities and those without by using relay operators or specialized equipment. Here's how TRS works:
User Initiates the Call: The person with a hearing or speech disability initiates a phone call using a text telephone (TTY), a computer with text-based communication software, or other specialized communication devices.
Dialing the Relay Service: Instead of dialing the recipient's number directly, the user dials a dedicated TRS phone number. This number connects them to a relay service provider.
Connects to a Relay Operator: When the user dials the TRS number, their call is routed to a relay operator at the relay service center. Relay operators are specially trained professionals who facilitate the conversation between the caller with a disability and the recipient.
User's Message: The person with a disability communicates their message to the relay operator using text, voice, or other appropriate means. For example, if they are using a TTY, they type their message, and if they use sign language, they sign to the relay operator.
Relay Operator Relays the Message: The relay operator relays the caller's message to the recipient using voice or text, depending on the recipient's preferences. If the recipient is using a standard telephone, the relay operator speaks the message to them. If the recipient is also using a TTY or similar device, the relay operator types the message.
Recipient Responds: The recipient, who may or may not have a hearing or speech disability, responds to the relay operator's message. They speak or type their response.
Relay Operator Relays Back: The relay operator then relays the recipient's response back to the original caller, again using the appropriate mode of communication.
Continued Conversation: The conversation continues in this manner, with the relay operator serving as an intermediary, until the communication is complete.
TRS is designed to be confidential and secure, and relay operators are trained to remain neutral and not to interpret or alter the content of the conversation. The goal is to provide individuals with disabilities the same level of access to telecommunications services as those without disabilities, ensuring equal communication opportunities.
There are various types of TRS services, including TTY-based relay, video relay services (VRS) for American Sign Language (ASL) users, and speech-to-speech relay for individuals with speech disabilities. TRS is an essential tool that helps people with hearing or speech disabilities participate in phone calls, access emergency services, make appointments, and communicate with family, friends, and colleagues like anyone else.
Teacher Retirement System (TRS): What It Is and How It Works
A Teacher Retirement System (TRS) is a pension plan for teachers and other public education employees. TRS plans typically provide retirement benefits such as a monthly pension, health insurance, and life insurance.
TRS plans are funded by contributions from both employees and employers. Employees typically contribute a percentage of their paycheck to the TRS plan, and their employer matches a portion of those contributions. The money in the TRS plan is invested, and the earnings from those investments are used to pay the retirement benefits of TRS members.
Exploring TRS: Understanding Your Retirement Benefits
TRS members typically have two types of retirement benefits: a service pension and a disability pension.
- Service pension: A service pension is a monthly payment that is based on a TRS member's years of service and salary. TRS members typically become eligible for a service pension at age 55 or 60, depending on their state's TRS plan.
- Disability pension: A disability pension is a monthly payment that is made to TRS members who become disabled and unable to work. TRS members are typically eligible for a disability pension if they have at least five years of service and their disability is work-related.
In addition to a service pension and a disability pension, TRS members may also be eligible for other benefits, such as health insurance, life insurance, and long-term care insurance.
Building a Secure Future: How TRS Can Support Your Retirement Goals
TRS plans can provide teachers and other public education employees with a secure retirement. The following are some of the benefits of participating in a TRS plan:
- Guaranteed income: A TRS pension is a guaranteed monthly income that TRS members receive for the rest of their lives. This can provide TRS members with financial security in retirement.
- Portability: TRS plans are portable, meaning that TRS members can take their TRS benefits with them if they move to another state. This can be helpful for TRS members who relocate for work or other reasons.
- Tax advantages: TRS contributions are typically tax-deferred, meaning that TRS members do not have to pay taxes on their contributions until they withdraw them in retirement. This can help TRS members save money on taxes.
TRS plans can be a valuable tool for teachers and other public education employees to save for retirement. By participating in a TRS plan, TRS members can build a secure financial future for themselves and their families.
Here are some tips for maximizing your TRS benefits:
- Start contributing to your TRS plan as early as possible. The earlier you start contributing, the more time your money has to grow.
- Increase your TRS contributions each year, if possible. This will help you save more money for retirement.
- Take advantage of the tax advantages of TRS plans.
- Review your TRS benefits regularly and make sure that you understand your options.
- Seek financial advice from a qualified professional to help you develop a retirement plan that meets your individual needs.