What is the process of transcription and translation?
Transcription and translation are fundamental processes in molecular biology that are essential for the synthesis of proteins, the building blocks of cells. These processes occur in all living organisms and are crucial for the transfer of genetic information from DNA to protein. Here's an overview of the transcription and translation process:
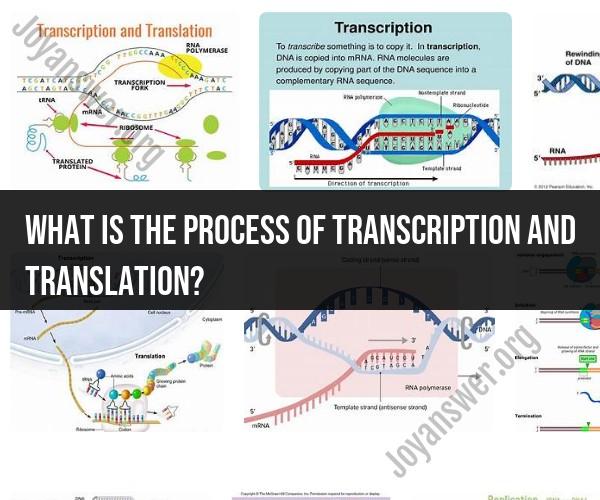
1. Transcription:
a. Initiation:
- Transcription begins in the cell's nucleus, where the DNA molecule serves as a template.
- RNA polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes a specific region on the DNA called the promoter and attaches to it.
- The DNA strands unwind, exposing a single-stranded template.
b. Elongation:
- RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template, synthesizing a complementary RNA molecule.
- As RNA polymerase moves, it adds nucleotides to the growing RNA strand based on the complementary base-pairing rules (A-U, C-G).
- This process continues until a termination signal is reached.
c. Termination:
- Transcription terminates when RNA polymerase encounters a termination signal on the DNA.
- The newly synthesized RNA molecule, called messenger RNA (mRNA), is released from the DNA template.
2. Post-Transcriptional Modifications (Optional):
- In eukaryotic cells, the initial mRNA transcript undergoes various modifications, including the removal of non-coding regions (introns) and the addition of a protective cap (5' cap) and a poly-A tail (3' polyadenylation).
3. Translation:
a. Initiation:
- Translation occurs in the cell's cytoplasm on ribosomes.
- The small ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA near the start codon (AUG), which codes for the amino acid methionine.
- An initiator tRNA molecule carrying methionine binds to the start codon on the mRNA.
b. Elongation:
- The large ribosomal subunit joins the small subunit, creating a functional ribosome.
- The ribosome moves along the mRNA in a 5' to 3' direction.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carrying specific amino acids bind to the mRNA codons via complementary base pairing.
- Peptide bonds form between adjacent amino acids, creating a growing polypeptide chain.
- The ribosome moves from codon to codon, and tRNA molecules continue to bring amino acids to the growing chain until a stop codon is encountered.
c. Termination:
- Translation terminates when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is reached on the mRNA.
- Release factors bind to the ribosome, causing the release of the completed polypeptide chain.
- The ribosome dissociates from the mRNA.
4. Protein Folding and Modification:
- The newly synthesized polypeptide chain may undergo folding, modifications, and assembly to become a functional protein.
- These processes can include post-translational modifications like phosphorylation, glycosylation, and proteolytic cleavage.
In summary, transcription is the process of copying genetic information from DNA to mRNA, which occurs in the cell's nucleus. Translation is the process of decoding the mRNA to synthesize a specific sequence of amino acids, forming a protein, and it takes place in the cytoplasm on ribosomes. Together, transcription and translation are the central dogma of molecular biology, representing the flow of genetic information from DNA to protein in living organisms.
1. The Molecular Ballet: Transcription and Translation in Cells
Transcription and translation are two essential processes that cells use to convert DNA into proteins. DNA is the genetic material that contains the instructions for building and maintaining all living organisms. Proteins are complex molecules that perform a wide range of functions in cells, including metabolism, signaling, and transport.
Transcription is the process of copying a gene from DNA into RNA. RNA is a similar molecule to DNA, but it is single-stranded and contains the ribose sugar instead of the deoxyribose sugar found in DNA.
Translation is the process of converting RNA into proteins. Each RNA molecule contains a sequence of nucleotides, which are the building blocks of RNA. The nucleotides are arranged in groups of three, called codons. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid.
During translation, the ribosome, a molecular machine in the cell, reads the codons on the RNA molecule and assembles the corresponding amino acids into a protein chain. The protein chain is then folded into its active three-dimensional structure.
2. Step-by-Step Guide to the Process of Transcription and Translation
Transcription
- RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of a gene.
- The DNA double helix unwinds to expose the template strand.
- RNA polymerase synthesizes a complementary RNA transcript, starting at the start codon and ending at the stop codon.
- The DNA double helix rewinds and the RNA transcript is released.
Translation
- The ribosome binds to the start codon on the RNA transcript.
- The ribosome moves along the RNA transcript, codon by codon.
- At each codon, the ribosome binds to a tRNA molecule carrying the corresponding amino acid.
- The amino acid is added to the growing protein chain.
- When the ribosome reaches the stop codon, the protein chain is released.
3. How Cells Convert DNA into Functional Proteins
Transcription and translation work together to convert DNA into functional proteins. The DNA contains the instructions for building the protein, and the RNA transcript is the blueprint that the ribosome uses to assemble the protein chain.
The proteins that are produced in cells are essential for all life processes. Proteins catalyze metabolic reactions, transport molecules across cell membranes, and signal between cells.
Conclusion
Transcription and translation are two fundamental processes that allow cells to convert DNA into functional proteins. These proteins perform a wide range of functions in cells, including metabolism, signaling, and transport.
Transcription and translation are complex processes, but they are essential for life. Without these processes, cells would not be able to produce the proteins that they need to survive and function properly.