What is transcription and translation?
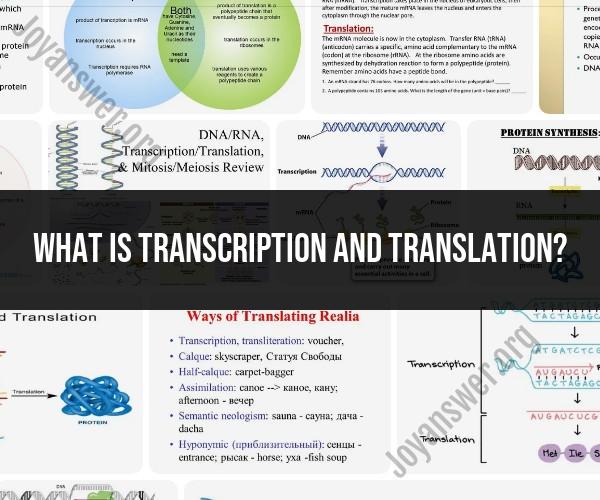
Transcription and translation are fundamental processes in molecular biology that are crucial for the synthesis of proteins, the building blocks of cells. These processes occur within a cell's nucleus and cytoplasm, involving the conversion of genetic information from DNA to proteins.
1. Transcription:
- Transcription is the first step in protein synthesis and takes place in the cell's nucleus.
- It involves the conversion of a specific segment of DNA into a complementary RNA molecule.
- The DNA segment that serves as a template for transcription is called a gene.
- An enzyme called RNA polymerase reads the DNA sequence and synthesizes a corresponding RNA molecule, following the base-pairing rules (A-U, C-G in RNA).
- The resulting RNA molecule is known as messenger RNA (mRNA) because it carries the genetic code or message from the DNA to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis will occur.
- Transcription also involves several regulatory elements, including promoters and enhancers, that control when and how a gene is transcribed.
2. Translation:
- Translation is the second step in protein synthesis and occurs in the cell's cytoplasm, specifically on ribosomes.
- The mRNA molecule synthesized during transcription serves as the template for translation.
- During translation, the genetic code carried by the mRNA is decoded to assemble a specific sequence of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins.
- The genetic code is read in groups of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or a signal to start or stop translation.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules play a critical role in translation. Each tRNA carries a specific amino acid and has an anticodon region that can base-pair with the complementary mRNA codon.
- Ribosomes facilitate the binding of tRNA molecules to the mRNA and catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids, forming a growing polypeptide chain.
- Translation continues until a stop codon is encountered, signaling the termination of protein synthesis.
In summary, transcription is the process of copying genetic information from DNA to mRNA within the nucleus, while translation is the process of using the mRNA template to synthesize a specific sequence of amino acids to form a protein in the cytoplasm. These two processes are tightly regulated and are essential for the proper functioning of living cells.
Transcription and Translation: Fundamental Processes in Biology
Transcription and translation are two of the most fundamental processes in biology. They are the processes by which genetic information encoded in DNA is converted into proteins, which are the workhorses of the cell.
Transcription is the process of copying DNA into RNA. RNA is a single-stranded molecule that is similar to DNA, but it uses the base uracil instead of thymine. Transcription takes place in the nucleus of the cell, where the DNA is located.
Translation is the process of converting RNA into proteins. Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are linked together in chains. Translation takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell, where the ribosomes are located. Ribosomes are the molecular machines that assemble proteins.
The Molecular Machinery of Transcription and Translation
Transcription and translation are complex processes that involve a number of different molecules. Here is a brief overview of the molecular machinery involved in each process:
Transcription
- RNA polymerase: RNA polymerase is the enzyme that catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA.
- Promoter: The promoter is a region of DNA that binds RNA polymerase and signals the start of transcription.
- Terminators: Terminators are regions of DNA that signal the end of transcription.
Translation
- Ribosomes: Ribosomes are the molecular machines that assemble proteins.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): tRNA molecules carry amino acids to the ribosome during translation.
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): mRNA molecules carry the genetic code for proteins.
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and Translation
The central dogma of molecular biology states that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to proteins. This means that the information encoded in DNA is used to make RNA, and the information encoded in RNA is used to make proteins.
Transcription and translation are essential for life. Without these processes, cells would not be able to make the proteins they need to survive and function.
Here is an example of how transcription and translation work together:
- A gene in the DNA is transcribed into mRNA.
- The mRNA travels to the cytoplasm of the cell.
- The mRNA binds to a ribosome.
- tRNA molecules carry amino acids to the ribosome.
- The ribosome assembles the amino acids into a protein.
- The protein is released from the ribosome.
The protein can then be used by the cell to perform a variety of functions, such as building new structures, transporting molecules, and catalyzing chemical reactions.
Transcription and translation are complex and fascinating processes that are essential for life. By understanding how these processes work, we can better understand how cells function and how diseases can arise.