What are the different types of Natural Sciences?
Natural sciences encompass a broad range of scientific disciplines that explore and study the natural world. These disciplines aim to understand the principles and processes that govern the physical and biological aspects of the universe. Here are some major types of natural sciences, categorized based on their primary focus:
Physical Sciences:
- Physics: Studies the fundamental principles governing matter, energy, space, and time.
- Chemistry: Investigates the properties, composition, structure, and changes of matter.
Earth Sciences:
- Geology: Examines the Earth's structure, composition, and processes, including the study of rocks, minerals, and landforms.
- Meteorology: Focuses on the study of weather patterns, atmospheric conditions, and climate.
- Oceanography: Studies the physical and biological aspects of the oceans, including marine life, currents, and ecosystems.
Biological Sciences:
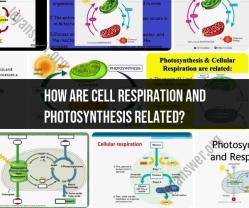
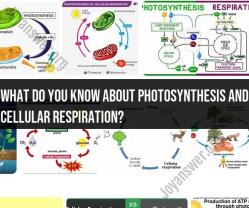
- Biology: Encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including the study of living organisms, their structure, function, growth, evolution, and interactions.
- Botany: Concentrates on the study of plants, including their classification, physiology, ecology, and evolution.
- Zoology: Focuses on the study of animals, covering their behavior, physiology, anatomy, and evolutionary history.
Environmental Science:
- Examines the interactions between living organisms and their environment, addressing issues related to conservation, sustainability, and the impact of human activities on ecosystems.
Astronomy:
- Studies celestial objects such as stars, planets, galaxies, and the larger universe. It includes observational and theoretical aspects.
Mathematical Sciences:
- While often considered a formal science, mathematics plays a crucial role in many natural sciences, providing tools for modeling, analysis, and prediction.
Interdisciplinary Sciences:
- Biogeochemistry: Combines principles from biology, geology, and chemistry to study the movement of elements and compounds in the Earth's systems.
- Astrobiology: Integrates elements of biology, chemistry, and astronomy to explore the potential for life beyond Earth.
Neuroscience:
- Investigates the structure and function of the nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord.
Materials Science:
- Examines the properties, structure, and applications of materials, with a focus on developing new materials for various purposes.
Chemical Engineering:
- Applies principles of chemistry, physics, and mathematics to design, produce, and use chemicals, materials, and energy.
These categories represent the diversity within the natural sciences, and many scientific investigations often involve interdisciplinary approaches, recognizing that the natural world is interconnected across various domains.
Exploring the Diverse Branches of Natural Sciences
Natural sciences encompass a broad spectrum of disciplines that seek to understand and explain the natural world around us. From the intricate workings of living organisms to the vast expanse of the cosmos, natural sciences provide a profound and ever-expanding body of knowledge. Let's delve into the fascinating branches of natural sciences and discover the wonders they unveil.
Biology: Understanding the Living World
Biology stands as the foundation of life science, exploring the diversity, structure, function, and evolution of living organisms. It encompasses a wide range of subfields, including:
Zoology: The study of animals, their behavior, and their interactions with the environment
Botany: The study of plants, their structure, physiology, and classification
Microbiology: The study of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi
Genetics: The study of heredity and variation in organisms
Ecology: The study of the interactions between organisms and their environment
Chemistry: Unraveling the Secrets of Matter
Chemistry delves into the composition, structure, and properties of matter, investigating the chemical reactions that shape our world. It encompasses various subfields, such as:
Inorganic Chemistry: The study of non-carbon-based compounds and their interactions
Organic Chemistry: The study of carbon-based compounds, including the building blocks of life
Analytical Chemistry: The development of methods to identify, measure, and analyze substances
Physical Chemistry: The application of physics to chemical phenomena, exploring energy changes and reaction rates
Biochemistry: The study of chemical processes that occur in living organisms
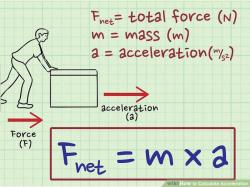
Physics: Delving into the Laws of Nature
Physics seeks to understand the fundamental laws that govern the universe, from the motion of objects to the behavior of light and matter. It encompasses diverse subfields, including:
Classical Mechanics: The study of the motion of objects under the influence of forces
Electromagnetism: The study of the interaction between electric charges and magnetic fields
Thermodynamics: The study of heat, energy transfer, and entropy
Quantum Mechanics: The study of the behavior of matter at the atomic and subatomic level
Cosmology: The study of the origin, evolution, and structure of the universe
Earth Science: Investigating Our Planet's Processes and Systems
Earth science encompasses the study of our planet's physical processes and systems, including the formation and composition of the Earth, its atmosphere, and its oceans. It encompasses various subfields, such as:
Geology: The study of the Earth's solid components, including its rocks, minerals, and landforms
Geophysics: The study of the Earth's physical properties, such as its magnetic field and gravitational forces
Meteorology: The study of the Earth's atmosphere, its weather patterns, and climate change
Oceanography: The study of the Earth's oceans, their currents, and the life they support
Environmental Science: The study of the interactions between human activities and the natural environment
These diverse branches of natural sciences provide a glimpse into the vast and interconnected web of life and the universe we inhabit. Through continuous exploration, experimentation, and innovation, natural scientists continue to unravel the mysteries of the natural world, expanding our understanding and shaping our future.