Is mRNA made during transcription or translation?
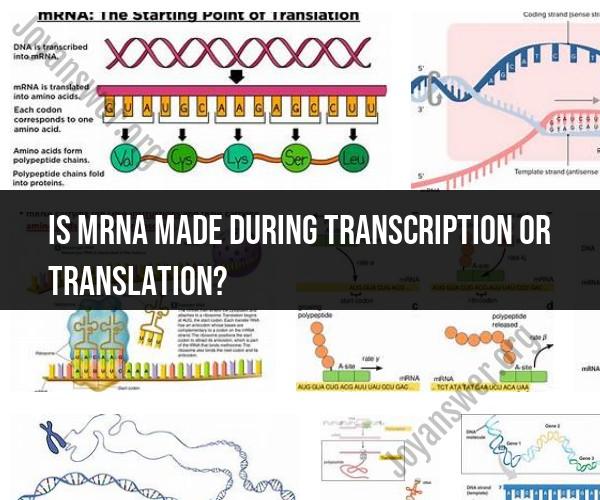
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is produced during the process of transcription, not during translation.
Here's a brief explanation of these two key processes in molecular biology:
Transcription: Transcription is the first step in protein synthesis. During transcription, a specific segment of DNA serves as a template to produce a complementary mRNA molecule. This mRNA molecule carries genetic information from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis (translation) will occur.
Translation: Translation is the process by which the genetic information carried by the mRNA is used to assemble a protein. This process takes place in the ribosomes, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules read the mRNA sequence and bring the corresponding amino acids to create a polypeptide chain, which eventually folds into a functional protein.
So, in summary, mRNA is synthesized during transcription and serves as the intermediary between DNA and protein production during translation.
mRNA Synthesis: Is It Part of Transcription or Translation?
mRNA synthesis is part of transcription. Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied into RNA. The resulting RNA molecule is called messenger RNA (mRNA). mRNA then carries the genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where it is translated into proteins.
The Role of mRNA in the Flow of Genetic Information
mRNA plays a vital role in the flow of genetic information from DNA to proteins. It is the intermediate molecule that carries the genetic code from the DNA to the ribosomes, where it is translated into proteins.
Proteins are essential for all life processes, so mRNA is essential for life itself.
Understanding the Timing of mRNA Production in the Cell
mRNA production in the cell is regulated by a variety of factors, including the cell's needs and the presence of external signals.
For example, if a cell needs to produce more of a certain protein, it will transcribe more mRNA for that protein. Similarly, if a cell is exposed to a stressor, such as infection or heat shock, it may transcribe specialized mRNAs that help the cell to cope with the stress.
mRNA production is also regulated by the cell cycle. During cell division, mRNA production is generally reduced. This is because the cell is busy replicating its DNA and other organelles, and it does not need to produce new proteins at the same rate.
Once cell division is complete, mRNA production resumes and the cell begins to produce new proteins to support its growth and function.