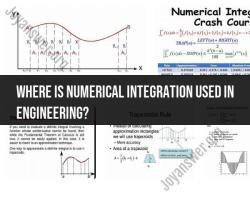
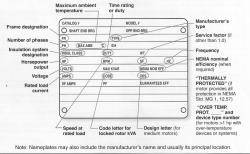
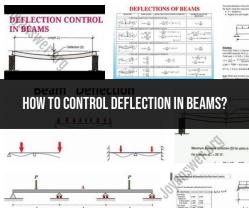
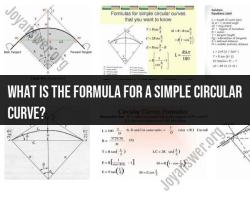
What is the difference between FPM and CFM?
FPM and CFM are units of measurement used in the fields of fluid dynamics and air handling to describe different aspects of airflow. Here's what each abbreviation stands for and the key difference between them:
FPM - Feet Per Minute:
- FPM stands for "Feet Per Minute."
- FPM is a unit of measurement used to express the velocity or speed of airflow. It represents how many linear feet of air pass by a specific point in one minute.
- FPM is commonly used to describe the velocity of air in a duct or pipe. It helps assess the speed of airflow within a confined space.
- For example, if you have an air duct with an airflow velocity of 500 FPM, it means that the air is moving at 500 linear feet per minute through that duct.
CFM - Cubic Feet Per Minute:
- CFM stands for "Cubic Feet Per Minute."
- CFM is a unit of measurement used to quantify the volume of airflow. It represents how many cubic feet of air pass through a specific point in one minute.
- CFM is often used to describe the capacity or volume of air moved by fans, HVAC systems, or other air-handling equipment.
- For example, if a fan is rated at 1,000 CFM, it means that the fan is capable of moving 1,000 cubic feet of air per minute.
Key Difference:The main difference between FPM and CFM is what they measure:
FPM (Feet Per Minute) measures the speed or velocity of airflow. It focuses on how quickly the air is moving past a specific point.
CFM (Cubic Feet Per Minute) measures the volume of airflow. It quantifies how much air is being moved in terms of cubic feet per minute.
In practical terms, when evaluating air handling systems, it's common to consider both FPM and CFM. The FPM measurement helps assess the efficiency and effectiveness of ductwork and the speed of airflow in specific areas. The CFM measurement is crucial for selecting the right equipment, such as fans or HVAC units, to meet the required airflow volume for a particular space or application.
FPM vs. CFM: Unpacking the Differences in Measurement
FPM stands for feet per minute, while CFM stands for cubic feet per minute. Both units of measurement are used to describe airflow, but they measure different things.
FPM measures the linear velocity of airflow, while CFM measures the volumetric flow rate of airflow. In other words, FPM measures how fast air is moving, while CFM measures how much air is moving.
To convert from FPM to CFM, you need to know the cross-sectional area of the duct or opening through which the air is flowing. The formula for converting FPM to CFM is:
CFM = FPM * Cross-sectional area
For example, if you have a duct with a cross-sectional area of 1 square foot and the air is flowing through the duct at 100 FPM, then the CFM of airflow in the duct is 100 CFM.
When to Use FPM and When to Use CFM in HVAC Systems
FPM is typically used to measure airflow velocity in ducts and other air passages. CFM is typically used to measure airflow volume in HVAC systems.
For example, you might use FPM to measure the airflow velocity in the ductwork of an HVAC system. You might use CFM to measure the airflow volume of an HVAC system's fan.
Navigating Airflow Measurements: FPM and CFM Explained
FPM and CFM are important measurements for HVAC systems because they can help to ensure that the system is operating properly. For example, if the airflow velocity in a duct is too high, it can cause noise and vibration. If the airflow volume in a duct is too low, it can lead to poor comfort levels.
HVAC professionals use FPM and CFM measurements to design and install HVAC systems that meet the specific needs of a building or space. They also use these measurements to troubleshoot and maintain HVAC systems.
Here are some additional examples of when to use FPM and CFM in HVAC systems:
- FPM:
- Measuring the airflow velocity in a duct
- Measuring the airflow velocity at a diffuser or grille
- Measuring the airflow velocity at a fan outlet
- CFM:
- Measuring the airflow volume of an HVAC system's fan
- Measuring the airflow volume of an HVAC system's supply duct
- Measuring the airflow volume of an HVAC system's return duct
Conclusion
FPM and CFM are important measurements for HVAC systems. They can help to ensure that the system is operating properly and that it is meeting the specific needs of a building or space.