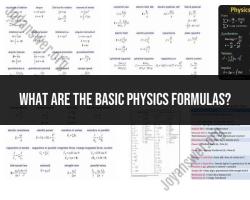
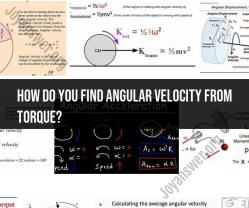
How to calculate equilibrium physics?
Calculating equilibrium in physics involves applying fundamental principles of classical mechanics, particularly Newton's laws of motion. Equilibrium occurs when the net force and net torque (rotational force) acting on an object are both equal to zero. Here are the steps to calculate equilibrium in physics:
Identify the Object or System: Determine the object or system you want to analyze for equilibrium. This could be a single object or a complex system of multiple objects.
Draw a Free Body Diagram (FBD): For each object within the system, draw a free body diagram. This diagram represents all the forces acting on the object. Label each force with its magnitude and direction.
Apply Newton's First Law: Newton's First Law of Motion states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. In equilibrium, the object is at rest, so the sum of all forces in both the horizontal and vertical directions must be zero. Mathematically, this is expressed as:
ΣF_x = 0 (for horizontal equilibrium)ΣF_y = 0 (for vertical equilibrium)
Here, ΣF_x represents the sum of all horizontal forces, and ΣF_y represents the sum of all vertical forces.
Apply Newton's Second Law: Newton's Second Law of Motion states that the net force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object times its acceleration (F = ma). Since the object is in equilibrium, its acceleration is zero, which means the net force is zero. Use this principle to set up equations for each direction (horizontal and vertical) to solve for any unknown forces or tensions.
Apply Newton's Third Law: Ensure that you account for all forces acting on the object, including contact forces (e.g., normal force, friction) and external forces (e.g., gravity, applied forces).
Check for Rotational Equilibrium: If the object is subject to torques (rotational forces), apply the same principles for torque as you did for forces. Torque is the product of the force applied to an object and the distance from the point of rotation. In rotational equilibrium, the sum of all torques must be zero. Mathematically, this is expressed as:
Στ = 0
Here, Στ represents the sum of all torques.
Solve for Unknowns: Use the equations you've set up to solve for any unknown forces or tensions. Ensure that the sum of forces and torques is zero in both the horizontal and vertical directions.
Check the Solution: After solving for unknowns, double-check that all forces and torques indeed add up to zero. If they do, the object or system is in equilibrium.
Remember to use appropriate units and take care with vector addition when calculating equilibrium in physics. The key is to balance all forces and torques to achieve a state of rest or uniform motion, which characterizes equilibrium.
To calculate equilibrium in physics, you need to use the following fundamental principles:
- Newton's first law of motion: An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced net force.
- Newton's second law of motion: The net force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration.
- Newton's third law of motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
To calculate equilibrium, you need to find the net force acting on the system. If the net force is zero, then the system is in equilibrium.
Here is a simple example of how to calculate equilibrium:
Example: A book is sitting on a table. What is the net force acting on the book?
The force of gravity is pulling the book downward, but the table is pushing upward with an equal force. Therefore, the net force acting on the book is zero and the book is in equilibrium.
Calculating equilibrium in more complex systems
Calculating equilibrium in more complex systems can be more challenging. For example, to calculate the equilibrium of a bridge, you would need to consider the weight of the bridge, the weight of the vehicles and pedestrians on the bridge, and the forces exerted by the wind and the water.
To calculate equilibrium in complex systems, you can use a variety of methods, including:
- Free body diagrams: A free body diagram is a diagram of an object or system that shows all of the forces acting on it. Free body diagrams can be used to visualize the forces acting on a system and to calculate the net force.
- Equations of equilibrium: The equations of equilibrium are mathematical equations that can be used to calculate the net force acting on a system. The equations of equilibrium are based on Newton's laws of motion.
- Computer simulations: Computer simulations can be used to model complex systems and to calculate the equilibrium of those systems.
Conclusion
Calculating equilibrium in physics can be challenging, but it is an important skill for engineers and scientists. By understanding the fundamental principles of equilibrium and how to calculate it, you can design systems that are stable and efficient.