What are the key terms in a level physics?
Advanced Level (A Level) Physics involves the study of fundamental principles and concepts related to the physical world. Here is a comprehensive overview of key terms in A Level Physics:
Scalars and Vectors:
- Scalar: A quantity with only magnitude (e.g., distance, speed).
- Vector: A quantity with both magnitude and direction (e.g., displacement, velocity).
Kinematics:
- Displacement: Change in position of an object.
- Velocity: Rate of change of displacement.
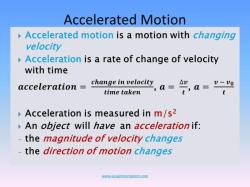
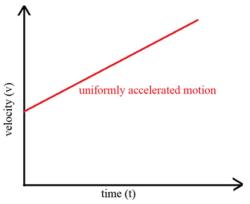
- Acceleration: Rate of change of velocity.
Dynamics:
- Force: A push or pull on an object.
- Newton's Laws of Motion: Describes the relationship between a body and the forces acting on it.
Energy:
- Work: Force applied over a distance.
- Energy: The capacity to do work.
- Power: Rate of doing work.
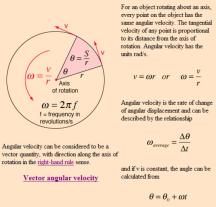
Circular Motion:
- Centripetal Force: Force directed towards the center of a circular path.
Gravitational Field:
- Gravitational Field Strength: Force experienced per unit mass in a gravitational field.
Electricity:
- Current: Flow of electric charge.
- Voltage (Potential Difference): Electric potential energy per unit charge.
- Resistance: Opposition to the flow of electric current.
- Ohm's Law: Describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
Magnetism:
- Magnetic Field: Region where a magnetic force is experienced.
- Magnetic Flux: Quantity representing the amount of magnetic field passing through a surface.
Waves:
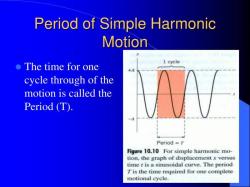
- Wave: Oscillation that transfers energy.
- Frequency: Number of oscillations per unit time.
- Amplitude: Maximum displacement from the equilibrium position.
- Wavelength: Distance between two successive points in a wave.
Optics:
- Refraction: Bending of light as it passes from one medium to another.
- Diffraction: Bending of waves around obstacles.
- Lens: Optical element that converges or diverges light.
Thermodynamics:
- Temperature: Measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
- Heat: Transfer of thermal energy between two bodies.
- First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred.
Nuclear Physics:
- Nuclear Fusion: Combination of atomic nuclei.
- Nuclear Fission: Splitting of atomic nuclei.
Quantum Physics:
- Quantum Mechanics: Study of particles on a very small scale.
- Wave-Particle Duality: Particles exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior.
Special Relativity:
- Theory developed by Albert Einstein: Describes the relationship between space and time in the presence of gravity.
Particle Physics:
- Subatomic Particles: Elementary particles such as quarks, leptons, and bosons.
This list is not exhaustive, and A Level Physics covers a wide range of topics. Understanding these key terms is fundamental to grasping the principles of physics at an advanced level.
What fundamental key terms are essential in A-Level Physics studies?
Mastering A-Level Physics requires a solid understanding of several fundamental key terms. Here are some of the most essential:
Mechanics:
- Displacement: Change in position of an object (vector quantity).
- Velocity: Rate of change of displacement (vector quantity).
- Acceleration: Rate of change of velocity (vector quantity).
- Force: Push or pull acting on an object, causing it to accelerate (vector quantity).
- Work: Energy transferred by a force acting through a distance.
- Power: Rate at which work is done.
- Momentum: Mass of an object multiplied by its velocity (vector quantity).
- Kinetic energy: Energy of an object in motion.
- Potential energy: Energy stored in an object due to its position or configuration.
- Gravitational field strength: Force per unit mass experienced by an object due to gravity.
Electricity and magnetism:
- Electric field: Region surrounding a charged particle where other charged particles experience a force.
- Magnetic field: Region surrounding a moving electric charge or a permanent magnet where other magnetic objects experience a force.
- Electric potential difference (voltage): Difference in electric potential energy between two points.
- Current: Flow of electric charge.
- Resistance: Opposition to the flow of electric current.
- Capacitance: Ability of a conductor to store electric charge.
- Inductance: Ability of a conductor to oppose changes in current.
- Electromagnetic force: Force between charged particles.
Waves and optics:
- Wave: Disturbance that transfers energy through space or matter.
- Amplitude: Maximum displacement of a wave from its equilibrium position.
- Wavelength: Distance between two consecutive points on a wave with the same phase.
- Frequency: Number of waves passing a point per unit time.
- Wave speed: Speed at which a wave travels through a medium.
- Refraction: Bending of a wave as it travels from one medium to another.
- Diffraction: Spreading of a wave as it passes through a narrow opening or around an obstacle.
- Interference: Interaction of two or more waves, resulting in a new wave pattern.
Thermodynamics:
- Temperature: Measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
- Heat: Transfer of thermal energy between objects at different temperatures.
- Internal energy: Total energy of all the particles in a substance.
- Entropy: Measure of disorder or randomness in a system.
- First law of thermodynamics: Law of conservation of energy, stating that the total energy of a closed system remains constant.
- Second law of thermodynamics: Law stating that the entropy of a closed system tends to increase over time.
These are just a few of the many key terms you'll encounter in A-Level Physics. Understanding these terms will provide a solid foundation for your studies and help you grasp more complex concepts.
Here are some resources to help you learn and remember these key terms:
- A-Level Physics textbooks and revision guides.
- Online resources such as Physics and Maths Tutor and Khan Academy.
- Flashcards and mnemonics.
- Practice quizzes and exams.
Remember, mastering key terms is an ongoing process. Be sure to review them regularly and practice applying them to solve problems.