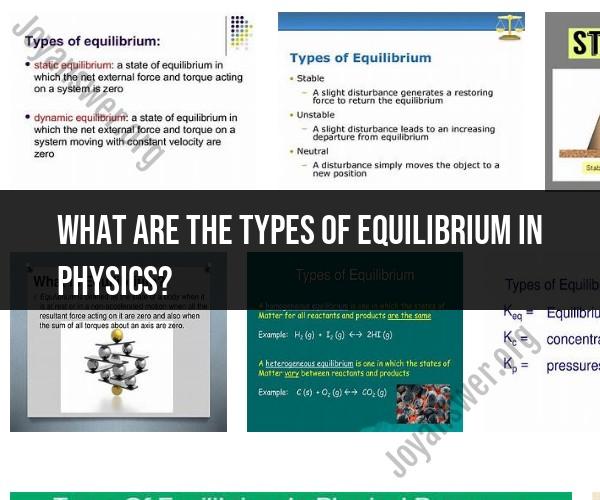
What are the types of equilibrium in physics?
In physics, there are primarily three types of equilibrium: stable equilibrium, unstable equilibrium, and neutral equilibrium. These concepts are often used to describe the stability or balance of an object or system when subjected to external forces. Here's a brief overview of each type:
Stable Equilibrium:
- In a stable equilibrium, a system or object returns to its original position or state when it is disturbed.
- If you think of a ball placed at the bottom of a bowl, it is in a stable equilibrium. If you push the ball slightly in any direction, it will roll back to the bottom of the bowl, returning to its original position.
Unstable Equilibrium:
- In an unstable equilibrium, a system or object is in balance, but any slight disturbance will cause it to move away from its current position.
- An example is a pencil standing on its tip. It can remain upright as long as it's perfectly balanced, but the slightest nudge will cause it to fall in any direction.
Neutral Equilibrium:
- In a neutral equilibrium, an object remains in its new position if disturbed, without returning to its original state.
- Imagine a ball placed at the center of a flat, horizontal surface. If you push the ball in any direction, it will stay where it is when you release it, neither returning to its original position nor moving further away.
These concepts of equilibrium are crucial in physics, particularly in understanding the stability of systems, the behavior of objects under the influence of forces, and the design of structures and mechanisms to ensure their stability and safety. The choice of equilibrium type depends on the specific requirements and characteristics of the system or object being analyzed.
There are three main types of equilibrium in physics:
- Static equilibrium: A system is in static equilibrium if it is at rest and the net force acting on it is zero.
- Dynamic equilibrium: A system is in dynamic equilibrium if it is not at rest but the net force acting on it is still zero.
- Thermal equilibrium: A system is in thermal equilibrium if it is at the same temperature as its surroundings and there is no net transfer of heat between them.
Static equilibrium is the most common type of equilibrium. It is the type of equilibrium that is usually associated with the word "equilibrium." Examples of static equilibrium include a book at rest on a table, a ball in the air at the apex of its trajectory, and a person standing on the ground.
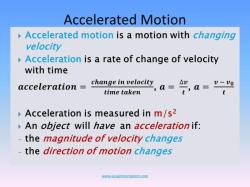
Dynamic equilibrium is a more subtle type of equilibrium. It is the type of equilibrium that occurs when a system is constantly changing but the overall state of the system remains the same. Examples of dynamic equilibrium include a bicycle moving at a constant speed, a water fountain, and a chemical reaction that has reached equilibrium.
Thermal equilibrium is the type of equilibrium that occurs when two systems are at the same temperature. When two systems are in thermal equilibrium, there is no net transfer of heat between them. Examples of thermal equilibrium include two cups of coffee at the same temperature and a person sitting in a room that is at the same temperature as their body.
Examples of equilibrium in physics:
- A ball rolling at a constant speed on a level surface is in dynamic equilibrium.
- A water balloon that is falling through the air but has not yet reached its terminal velocity is in dynamic equilibrium.
- A person standing on a skateboard that is rolling at a constant speed is in dynamic equilibrium.
- A rock that is sitting on a ledge is in static equilibrium.
- A cup of coffee that is sitting on a table and is at the same temperature as the room is in thermal equilibrium.
Equilibrium is an important concept in physics because it helps us to understand how systems behave. By understanding the different types of equilibrium, we can design systems that are stable and efficient.