What is the best temperature for photosynthesis?
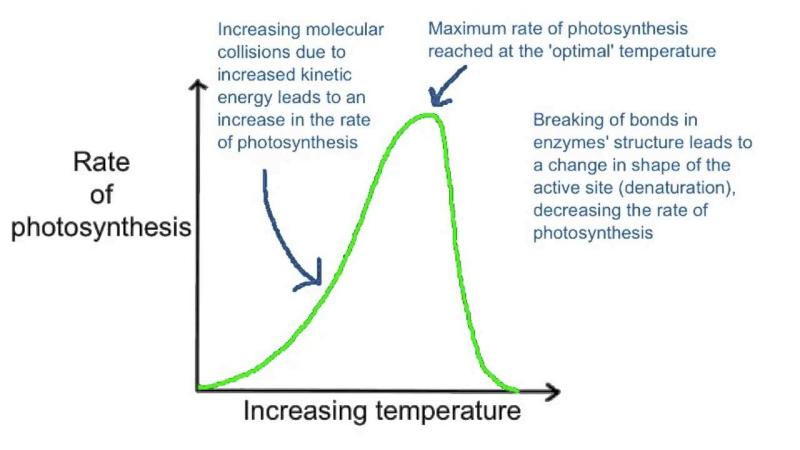
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy to fuel their growth, is influenced by temperature. While plants can perform photosynthesis across a range of temperatures, there is an optimal temperature at which this process is most efficient. The ideal temperature for photosynthesis varies somewhat among different plant species, but generally falls within the range of 68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit (20 to 25 degrees Celsius).
Here are some key points to consider regarding temperature and photosynthesis:
Optimal Temperature Range:
- The optimal temperature for photosynthesis falls between 68 and 77 degrees Fahrenheit (20 to 25 degrees Celsius). Within this range, the enzymes involved in photosynthesis function most effectively.
Colder Temperatures:
- Photosynthesis can still occur at lower temperatures, but the rate is generally slower. Cold temperatures can slow down the metabolic processes within the plant, including photosynthesis.
Warmer Temperatures:
- While photosynthesis can continue at temperatures above the optimal range, excessively high temperatures can have a negative impact. In some cases, high temperatures can lead to a process known as photorespiration, which reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis.
Species Variability:
- Different plant species may have slightly different temperature optima for photosynthesis. Some plants, especially those adapted to colder climates, may have optimal temperatures at the lower end of the range.
Light Intensity and Quality:
- The efficiency of photosynthesis is also influenced by light intensity and quality. Adequate light, along with optimal temperature, is crucial for maximizing photosynthetic rates.
Carbon Dioxide Availability:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a key ingredient in photosynthesis. While temperature is important, the availability of CO2 is also a factor that can influence the rate of photosynthesis.
Adaptations to Environmental Conditions:
- Some plants have adaptations that allow them to thrive in specific environmental conditions. For example, certain plants are adapted to higher temperatures and may have a higher temperature optimum for photosynthesis.
It's important to note that plants are adaptable, and their growth and photosynthetic rates can be influenced by various environmental factors, including temperature. Additionally, different stages of plant development (seed germination, vegetative growth, flowering) may have different temperature requirements.
For specific information on the optimal temperature for photosynthesis for a particular plant species, it is advisable to consult plant-specific literature or resources provided by agricultural extension services. Additionally, controlled experiments and observations can help growers optimize conditions for the plants they are cultivating.
What is the ideal temperature for photosynthesis to occur?
The ideal temperature for photosynthesis to occur is between 20-40°C (68-104°F). At these temperatures, the enzymes involved in photosynthesis are most active and the rate of photosynthesis is highest.
How does temperature affect the efficiency of the photosynthetic process?
Temperature affects the efficiency of the photosynthetic process in a number of ways.
- Enzymatic activity: Enzymes are proteins that catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions. The rate of enzymatic activity increases with temperature, up to a point. However, if the temperature gets too high, the enzymes can denature (lose their shape and function).
- Membrane fluidity: The membranes of plant cells are made up of phospholipids, which are molecules with a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-fearing) tail. At low temperatures, the phospholipids are tightly packed together and the membrane is rigid. This can make it difficult for molecules to move across the membrane. However, as the temperature increases, the phospholipids become more fluid and the membrane becomes more flexible. This makes it easier for molecules to move across the membrane, which can improve the efficiency of photosynthesis.
- Solubility of gases: The gases carbon dioxide and oxygen are required for photosynthesis. The solubility of gases in water decreases with temperature. This means that less carbon dioxide and oxygen will be dissolved in the water at higher temperatures, which can reduce the efficiency of photosynthesis.
Are there temperature thresholds that can hinder photosynthesis?
Yes, there are temperature thresholds that can hinder photosynthesis. At temperatures below 5°C (41°F), the rate of photosynthesis is very slow. This is because the enzymes involved in photosynthesis are not very active at low temperatures. At temperatures above 45°C (113°F), the enzymes involved in photosynthesis denature and the rate of photosynthesis drops to zero.
In addition to these temperature thresholds, there are other factors that can affect the efficiency of photosynthesis, such as the availability of light and water, the nutrient status of the plant, and the presence of pollutants.