What are three factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a complex process that occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria, converting light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Several factors influence the rate of photosynthesis. Here are three key influencers:
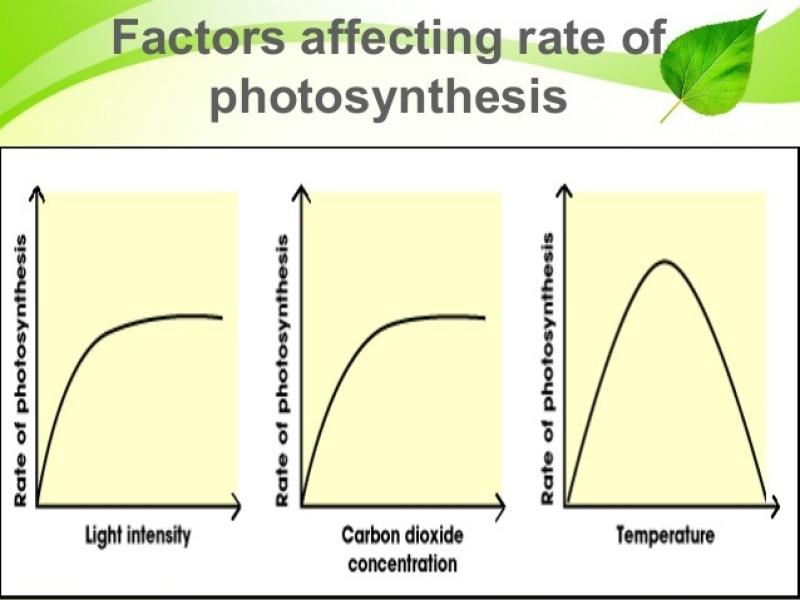
Light Intensity:
- Light is a crucial factor in photosynthesis because it provides the energy needed to drive the process. As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis generally increases, up to a certain point. Beyond the saturation point, further increases in light intensity may not result in a corresponding increase in the rate of photosynthesis.
Carbon Dioxide Concentration:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is one of the raw materials required for photosynthesis. As the concentration of carbon dioxide increases, the rate of photosynthesis typically increases. However, like light intensity, there is also a saturation point, and further increases in carbon dioxide concentration may not continue to stimulate photosynthesis.
Temperature:
- Temperature influences the speed of chemical reactions, including those involved in photosynthesis. Generally, as temperature rises, the rate of photosynthesis increases. However, there is an optimal temperature range for photosynthesis, and beyond this range, the rate can decline. Extremely high temperatures can denature enzymes involved in the process, leading to a decrease in photosynthetic activity.
These three factors—light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature—are often referred to as limiting factors. The rate of photosynthesis is limited by the factor that is in the shortest supply relative to the needs of the plant. Therefore, to maximize the rate of photosynthesis, it's important to ensure that these factors are within the optimal ranges for the specific plant species. Additionally, other factors such as water availability, nutrient levels, and the type of plant also play roles in influencing photosynthesis.
1. Three Key Factors Influencing Photosynthesis Rate
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, is essential for life on Earth. The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by several environmental factors, but the three most significant ones are:
Light intensity: Light provides the energy for photosynthesis to occur. As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis also increases up to a certain point, after which it reaches a plateau. Excessive light can even damage the plant's photosynthetic machinery.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration: CO2 is the raw material for photosynthesis. As CO2 concentration increases, the rate of photosynthesis also increases, up to a certain point. However, at very high CO2 concentrations, photosynthesis can become inhibited.
Temperature: Temperature plays a crucial role in enzyme activity. Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions. In photosynthesis, enzymes are responsible for converting light energy into chemical energy. As temperature increases, enzyme activity initially increases, and so does the rate of photosynthesis. However, at excessively high temperatures, enzymes denature and lose their function, leading to a decrease in photosynthesis.
2. Impact of Light Intensity, CO2 Levels, and Temperature
Light Intensity:
Increasing light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis until a certain point, known as the light saturation point. Beyond this point, the rate of photosynthesis plateaus due to the plant's inability to absorb and utilize all the available light energy. Excessive light can even damage the plant's photosynthetic machinery.
Carbon Dioxide Levels:
Increasing carbon dioxide concentration generally increases the rate of photosynthesis, as it provides more raw material for the process. However, at very high CO2 concentrations, photosynthesis can become inhibited due to the oversaturation of enzymes.
Temperature:
Temperature affects the activity of enzymes involved in photosynthesis. Within a certain range, increasing temperature increases enzyme activity and, consequently, the rate of photosynthesis. However, at excessively high temperatures, enzymes denature and lose their function, leading to a decrease in photosynthesis.
3. Optimal Conditions for Maximizing Photosynthesis Rate
To maximize the rate of photosynthesis, it is essential to provide plants with optimal conditions for each of the three key factors:
Light Intensity: Provide plants with adequate light, but avoid excessive exposure, which can lead to photoinhibition.
Carbon Dioxide Levels: Maintain a moderate CO2 concentration in the surrounding environment to provide sufficient raw material for photosynthesis without causing inhibition.
Temperature: Maintain a temperature within the plant's optimal range for enzyme activity. This range varies depending on the plant species.