What is the formula for cellular respiration and photosynthesis?
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are two fundamental biological processes that involve the conversion of energy between different forms in living organisms. Here's an overview of both processes along with their basic formulas:
Photosynthesis:
- Definition: Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen.
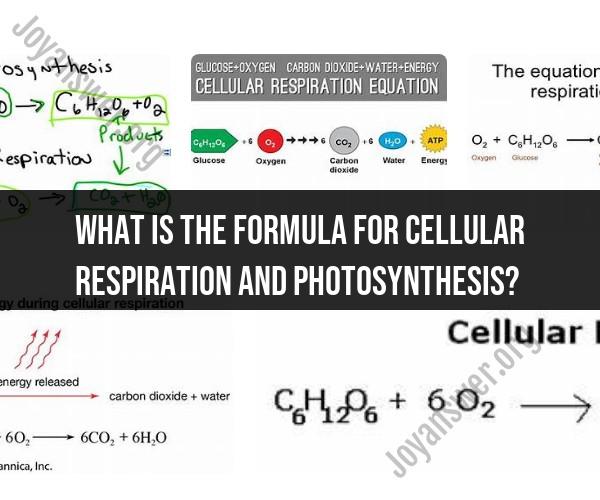
- Formula: The overall chemical equation for photosynthesis can be represented as:
- 6 CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6 H2O (water) + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 (oxygen)
- Stages:
- Light Reactions: In the presence of sunlight, chloroplasts in plant cells absorb light energy and use it to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen ions while producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is an energy carrier molecule.
- Calvin Cycle (Dark Reactions): This phase uses the ATP and hydrogen ions produced in the light reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose through a series of chemical reactions.
Cellular Respiration:
- Definition: Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other organic molecules to produce energy in the form of ATP. It occurs in all living cells.
- Formula: The overall chemical equation for cellular respiration is:
- C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 (oxygen) → 6 CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6 H2O (water) + ATP (energy)
- Stages:
- Glycolysis: In the cytoplasm, glucose is partially broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, and a small amount of ATP is generated.
- Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle): In the mitochondria, pyruvate is further oxidized to release carbon dioxide, generating additional ATP and electron carriers (NADH and FADH2).
- Electron Transport Chain: Electron carriers produced in the previous steps transfer electrons to the electron transport chain, located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This process generates a large amount of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
Key Points:
- Photosynthesis captures energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, storing energy in the form of chemical bonds.
- Cellular respiration releases the energy stored in glucose and other organic molecules, using oxygen to produce ATP, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Together, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected processes, as the oxygen produced in photosynthesis is used in cellular respiration, and the carbon dioxide produced in respiration is used in photosynthesis.
- These processes are vital for the energy balance in ecosystems, with photosynthesis being the basis of food chains and cellular respiration returning carbon and energy to the environment.
Understanding these processes is crucial in biology, as they are fundamental to the energy flow within living organisms and ecosystems.