What is the universal law of gravitational force?
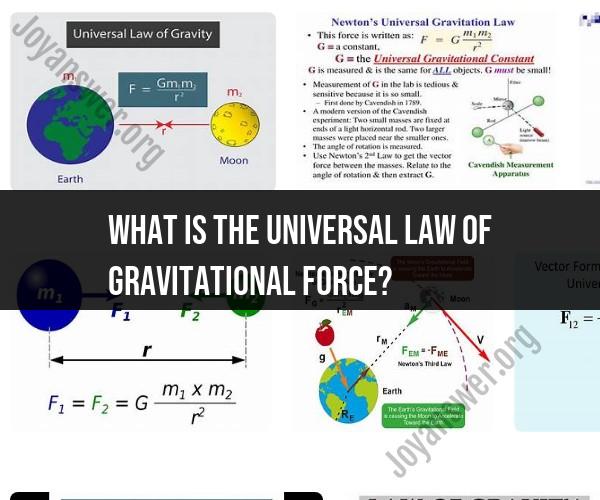
The universal law of gravitational force, also known as Newton's law of universal gravitation, is a fundamental principle in physics formulated by Sir Isaac Newton in the late 17th century. This law describes the attractive force of gravity between two objects with mass and is applicable to all objects with mass in the universe. The law can be stated as follows:
Every point mass attracts every other point mass by a force acting along the line intersecting both points. The force is directly proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Mathematically, the law can be expressed as:
Where:
- is the gravitational force between two objects.
- is the gravitational constant, a constant value that is approximately equal to in the International System of Units (SI).
- and are the masses of the two objects.
- is the distance between the centers of the two objects.
Key points to understand about the universal law of gravitational force:
Inverse Square Law: The force of gravity diminishes as the distance between the two objects increases, following an inverse square relationship. This means that if you double the distance between two objects, the gravitational force decreases to one-fourth of its original strength.
Proportional to Mass: The force of gravity is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the two objects. This means that if either of the masses is increased, the gravitational force between them also increases.
Universal Applicability: This law applies to all objects with mass, whether they are celestial bodies like planets, stars, and galaxies, or everyday objects on Earth. It is a universal law because it governs the gravitational interactions between all masses in the universe.
Fundamental to Celestial Mechanics: Newton's law of universal gravitation is fundamental to our understanding of celestial mechanics. It explains the orbits of planets around the sun, the motion of moons around planets, and many other gravitational interactions in the cosmos.
Superseded by General Relativity: While Newton's law of gravitation works well for most everyday situations and celestial mechanics, it was superseded by Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity in the early 20th century. General relativity provides a more accurate description of gravitation, particularly in extreme conditions or where high precision is required.
Nevertheless, Newton's law of universal gravitation remains a fundamental concept in physics and is still widely used for most practical purposes. It forms the basis for understanding and calculating gravitational forces in a wide range of applications.
The Universal Law of Gravitational Force: Explained
The Universal Law of Gravitation is a physical law that states that every point mass in the universe attracts every other point mass with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The law was first formulated by Isaac Newton in 1687 and was published in his book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ("Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy").
The Universal Law of Gravitation is one of the most fundamental laws of physics and it has been used to explain a wide range of phenomena, from the motion of planets and moons to the formation of galaxies.
Newton's Universal Law: Understanding Gravitational Attraction
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation is a universal law, which means that it applies to all objects in the universe, regardless of their mass or composition.
The law states that the force of gravity between two objects is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
This means that the more massive two objects are, the stronger the force of gravity between them will be. And the closer two objects are to each other, the stronger the force of gravity between them will be.
The force of gravity is a central force, which means that it acts along the line connecting the centers of mass of the two objects.
Gravity's Fundamental Principle: The Universal Law of Gravitational Force
The Universal Law of Gravitation is one of the most fundamental laws of physics. It is a universal law, which means that it applies to all objects in the universe, regardless of their mass or composition.
The law states that the force of gravity between two objects is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The Universal Law of Gravitation has been used to explain a wide range of phenomena, from the motion of planets and moons to the formation of galaxies.
Here are some examples of how the Universal Law of Gravitation is used in the real world:
- To calculate the orbits of planets and moons
- To design spacecraft and satellites
- To predict the trajectories of comets and asteroids
- To study the formation of galaxies and clusters of galaxies
- To measure the mass of distant objects, such as black holes and neutron stars
The Universal Law of Gravitation is a powerful tool that allows us to understand and predict the motion of objects in the universe.