Why does the gravitational force move in the direction of acceleration?
The gravitational force does not move in the direction of acceleration; rather, the gravitational force is the cause of the acceleration. This is a fundamental concept in physics, often described by Newton's second law of motion and the law of universal gravitation.
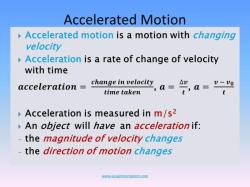
Newton's Second Law of Motion: This law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. Mathematically, it can be expressed as F = ma, where F is the net force, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration. In the context of gravitational force, this law tells us that an object will accelerate when subjected to a gravitational force.
Law of Universal Gravitation: This law, formulated by Sir Isaac Newton, describes the force of gravity between two objects. It states that every object with mass attracts every other object with mass, and the force of attraction is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Mathematically, it can be expressed as F = (G * m1 * m2) / r^2, where F is the gravitational force, G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, and r is the distance between their centers. This law explains the origin of the gravitational force.
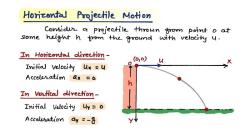
When an object is in a gravitational field, such as the Earth's gravitational field, it experiences a gravitational force directed toward the center of the massive object (e.g., the Earth). This force is responsible for the object's acceleration toward the center of the Earth. The gravitational force is what causes objects to fall when dropped, as it accelerates them in the direction of the Earth's center.
In summary, the gravitational force itself is responsible for the acceleration of objects in a gravitational field. It's not that the force "moves" in the direction of acceleration; rather, the presence of the force causes the acceleration, and the direction of that acceleration is toward the center of the massive object generating the gravitational field, as described by Newton's laws.
The following are some answers to your questions:
Why does gravitational force act in the direction of acceleration?
Gravitational force acts in the direction of acceleration because it is the force that causes objects to accelerate towards the center of mass of another object. The center of mass of an object is the point where all of its mass is evenly distributed. The more mass an object has, the stronger its gravitational force.
How is the relationship between gravity and acceleration described in physics?
The relationship between gravity and acceleration is described by Newton's second law of motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This means that the more force acting on an object, the faster it will accelerate. The more mass an object has, the slower it will accelerate.
What are the principles governing the direction of gravitational forces in objects?
The direction of gravitational forces in objects is governed by the principle of mass attraction. This principle states that any two objects with mass will attract each other with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The direction of the gravitational force is always towards the center of mass of the more massive object.
So, the reason why gravitational force acts in the direction of acceleration is because it is the force that causes objects to accelerate towards the center of mass of another object. The more mass an object has, the stronger its gravitational force. The relationship between gravity and acceleration is described by Newton's second law of motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. The direction of gravitational forces in objects is governed by the principle of mass attraction, which states that any two objects with mass will attract each other with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The direction of the gravitational force is always towards the center of mass of the more massive object.